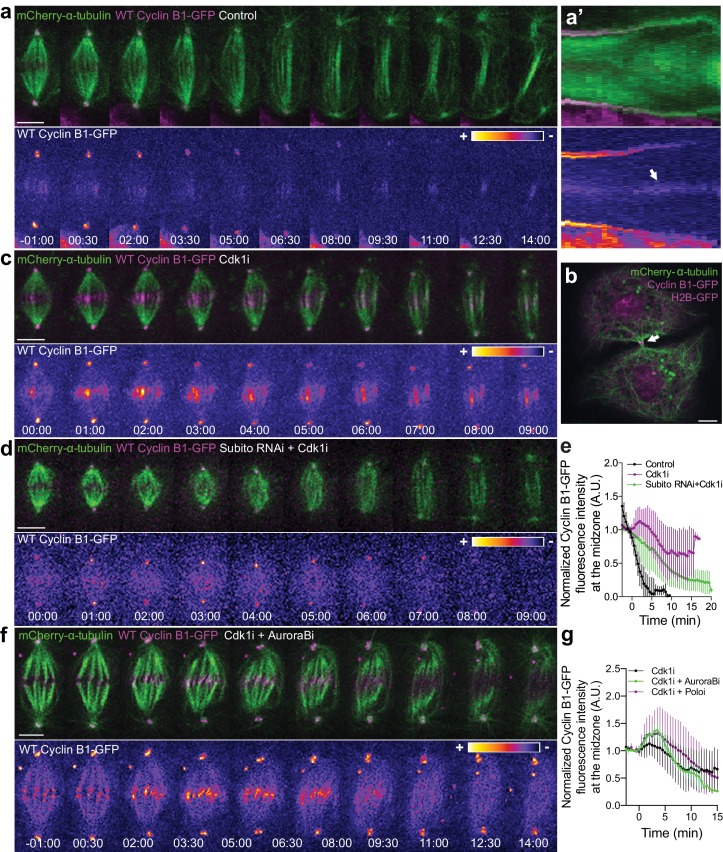
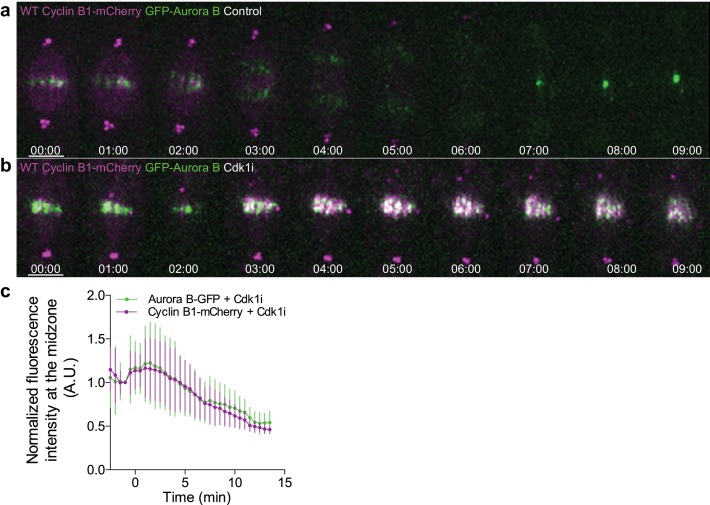
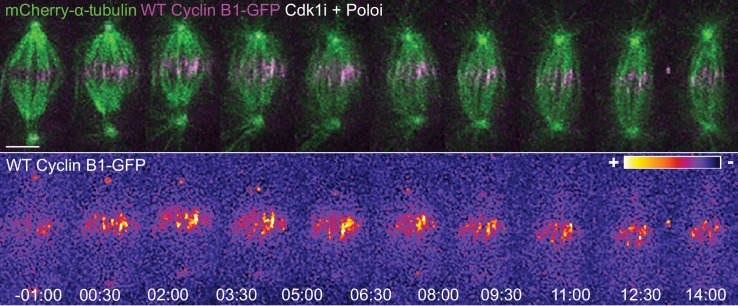
Figure 7. Cyclin B1 localization at the spindle midzone depends on Aurora B localization and activity during anaphase.
(a) Control Drosophila S2 cell stably expressing Cyclin B1-GFP/mCherry-α-tubulin showing a faint pool of Cyclin B1-GFP at the spindle midzone/midbody. (a’) Collapsed kymograph of the cell in a where Cyclin B1-GFP can be visualized at the spindle midzone/midbody. (b) Snapshot of a live Drosophila S2 cell expressing Cyclin B1-GFP/mCherry-α-tubulin where a midbody pool of Cyclin B1-GFP can be detected before completion of cytokinesis. (c) Drosophila S2 cell treated with Cdk1 inhibitor during metaphase. Cyclin B1 is not fully degraded and becomes visibly associated with midzone microtubules as cells are forced to exit mitosis. (d) Cdk1 inhibition at metaphase in a Drosophila S2 cell expressing Cyclin B1-GFP/mCherry-α-tubulin after Subito/Mklp2 depletion by RNAi. The Cyclin B1 midzone localization is no longer detectable. (e) Quantification of Cyclin B1-GFP fluorescence intensity measured at the spindle midzone (identified by the mCherry-α-tubulin signal) in untreated (n = 11 cells), Cdk1 inhibited cells (n = 10 cells) and Cdk1 inhibition after Subito/Mklp2 depletion (n = 12 cells, pooled from two independent experiments). (f) Drosophila S2 cells treated with Cdk1 inhibitor during metaphase and Aurora B inhibitor 4 min after Cdk1 inhibition. For all conditions, Cyclin B1-GFP signal is highlighted with the LUT ‘fire’. Scale bar is 5 μm. (g) Quantification of Cyclin B1-GFP fluorescence intensity measured at the spindle midzone in Cdk1 inhibited cells (n = 10 cells), Cdk1 + Aurora B inhibition (n = 11 cells) and Cdk1 + Polo inhibition (n = 10 cells).