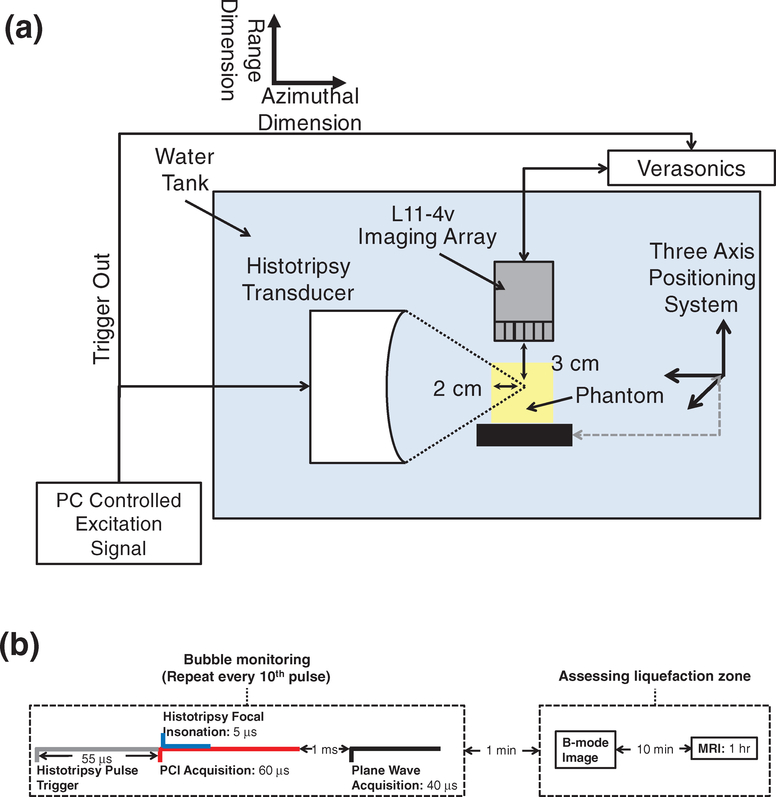
Figure 2.
(a) Side view of experimental setup for red blood cell (RBC) phantom insonation with a therapeutic ultrasound transducer. RBC layers of the phantoms were oriented parallel to the direction of ultrasound propagation from the histotripsy source. Fiducial markers embedded within the agarose were used to register diagnostic ultrasound and magnetic resonance (MR) images to digital photographs of phantoms post-insonation. The imaging plane of the L11–4v imaging array was registered to the RBC layers and visualized bubble activity along the acoustic axis of the histotripsy source. (b) Timeline of all image data acquisition. Passive and plane wave acquisitions were acquired every tenth histotripsy pulse due to data transfer rate limitations. Post hoc conventional B-mode images were acquired within 1 min of the histotripsy insonation. Samples were transferred to the MR scanner within 10 min, and MR images were acquired over the course of 1 h.