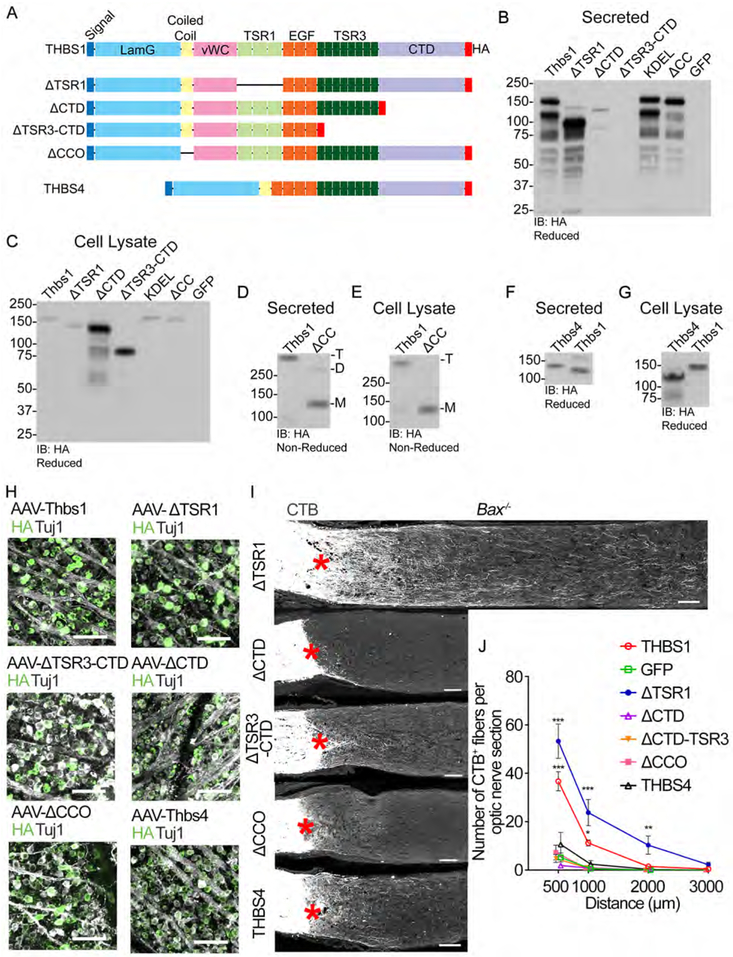
Figure 7: THBS1’s regenerative effects require trimerization and CTD, but not TSR1 domains.
(A) A schematic of THBS1 mutants investigated. All constructs contain the N-terminal signal peptide and have a C-terminal HA tag. Laminin G domain (LamG), oligomerization coiled coil (CC) domain, von Willebrand complex like domain (vWC), thrombospondin type 1 repeat domain (TSR1), epidermal growth factor-like repeat domains (EGF), type 3 repeat domain (TSR3), and the thrombospondin C-terminal domain (CTD). THBS4 is shown for comparison to THBS1.
(B-E) Validation of THBS1 constructs. Wild-type and mutant THBS1 vectors were expressed in HEK293T cells. All blots are immunoblotted (IB) for HA. (B and D) Secreted proteins from conditioned media. (C and E) Proteins from cell lysate. (B and C) Expression of THBS1, THBS1-ΔTSR1, THBS1-ΔCTD, THBS1-ΔTSR3-CTD, THBS1-KDEL, THBS1ΔCC, and GFP. Proteins reduced with DTT. THBS1-KDEL (nuclear exclusion sequence) was included to see if this form retains THBS1 expression inside the cells (refer to Discussion). (D and E) THBS1 and THBS1ΔCC were blotted under non-reducing conditions to validate oligomerization. Predicted oligomerization: M: monomeric, D: dimeric, and T: trimeric.
(F and G) Size validation of THBS4 construct. (F) Secreted proteins from conditioned media. (G) Proteins from cell lysate.
(H) Representative retinal whole mount images from mice injected with AAVs expressing various THBS forms stained for HA (green) and Tuj1 (grey). Scale bars, 100 μm.
(I) Images of optic nerve sections showing CTB-labeled axons (grey) in mice injected with AAV-THBS1ΔTSR1, AAV- THBS1ΔCTD, AAV- THBS1ΔTSR3-CTD, AAV- THBS1ΔCC or AAV-THBS4. Asterisks, lesion site. Scale bars, 100 μm.
(J) Quantification of axon regeneration for (I). Average number of CTB+ fibers per optic nerve section. ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post-hoc vs AAV-GFP, * p≤0.05, ** p≤0.01, *** p<0.001. n=5 for AAV-GFP, AAV-THBS1, AAV-THBS1ΔCTD, and AAV-THBS4, 4 for AAV-THBS1ΔTSR1, AAV-THBS1ΔTSR3-CTD, and AAV-THBS1ΔCC. Error bars, SEM.