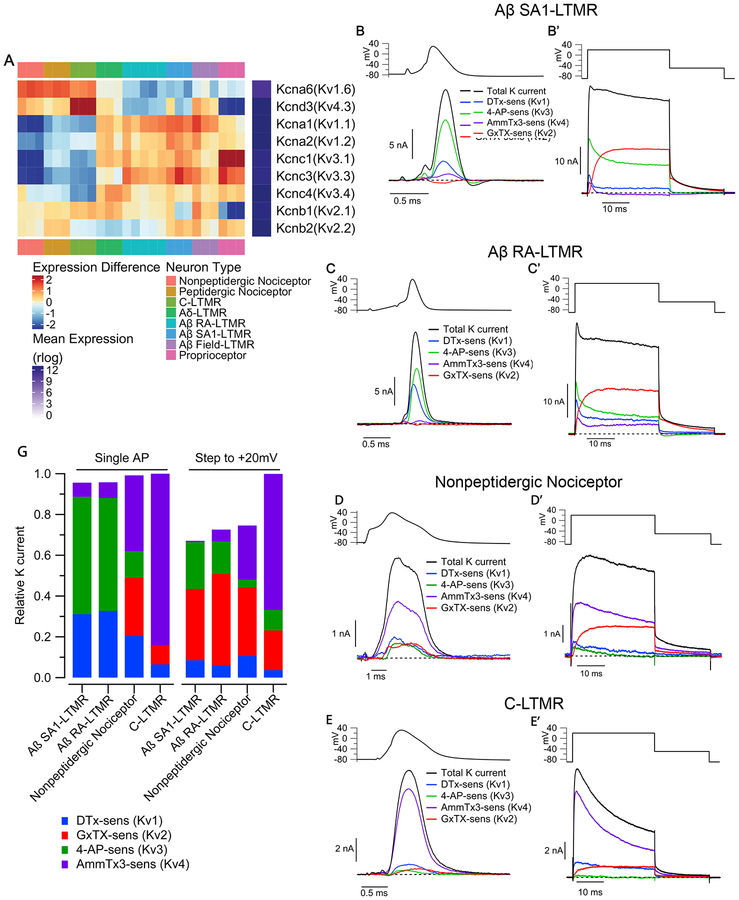
Figure 5. Kv channel families differentially contribute to outward current in sensory neuron subtypes.
(A) Heatmap depicting expression patterns of the most abundantly expressed Kv1, Kv2, Kv3 and Kv4 subunits. Plotting scheme is as Figure 2D.
(B-E) Components of Kv current during the AP of sensory neuron subtypes. Currentwas evoked by AP waveforms (previously recorded in a different cell of each type), and components of current were isolated by sequential cumulative application of 100 nM α-Dendrotoxin (DTX), 100 μM 4-aminopyridine (4-AP), 3 μM AmmTx3, and 100 nM Guangxitoxin-1E (GxTX) to identify Kv1, Kv3, Kv4, and Kv2 currents, respectively. (B’-E’) Currents evoked by a step depolarization to +20 mV (30 ms), applied in parallel with the AP commands in the same cells as B-E.
(F) Stacked bar plots showing the average fraction of total outward K+ current carried by Kv1, Kv2, Kv3, Kv4 channels in Aβ SA1-LTMRs (AP waveform: 31 ± 3% Kv1, 0 ± 1% Kv2, 59 ± 3% Kv3, 7 ± 1% Kv4; Step to +20 mV: 9 ± 2% Kv1, 35 ± 3% Kv2, 22 ± 3% Kv3, 1 ± 1% Kv4; n=15), Aβ RA-LTMRs (AP waveform: 33 ± 4% Kv1, 0 ± 2% Kv2, 58 ± 4% Kv3, 8 ± 2% Kv4; Step to +20 mV: 6 ± 3% Kv1, 45 ± 8% Kv2, 16 ± 7% Kv3, 6 ± 3% Kv4; n=11), MrgD+ nonpeptidergic nociceptors (AP waveform: 20 ± 4% Kv1, 29 ± 6% Kv2, 13 ± 3% Kv3, 37 ± 6% Kv4; Step to +20 mV: 11 ± 3% Kv1, 34 Kv4; n=11; mean ± SEM). Current contributions were quantified by integrating the currents during the AP or the 30ms step depolarization.