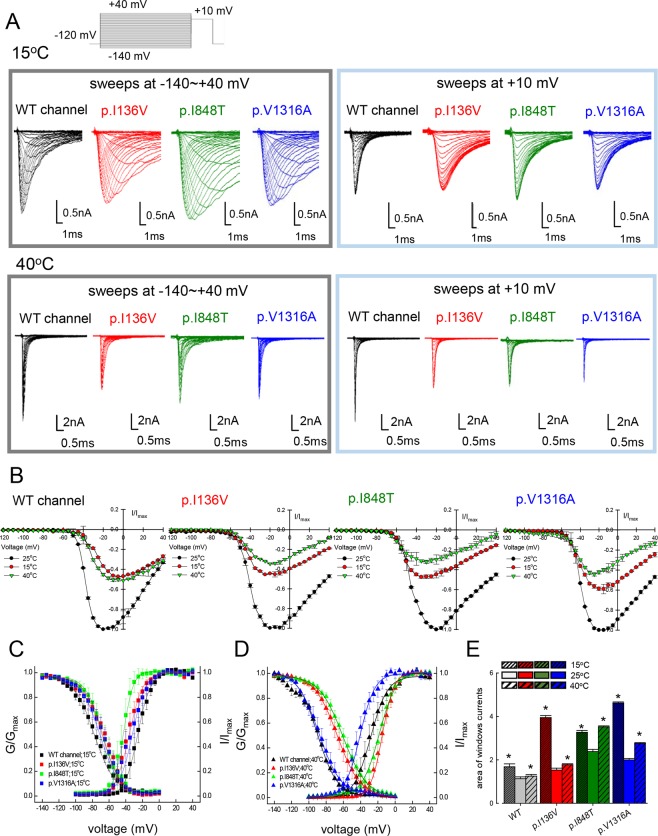
Figure 2.
Activation and inactivation curves of WT, p.I136V, p.I848T, and p.V1316A mutant channels at 15 °C and 40 °C. (A) Sample sweeps for the making of the activation (left panel) and inactivation (right panel) curves of the WT, p.I136V, p.I848T, and p.V1316A mutant channels at 15 °C or 40 °C. (B) The normalized current-voltage (I/V) curves of the WT, p.I136V, p.I848T, and p.V1316A mutant channels at 25 °C, 15 °C, or 40 °C are constructed by plotting the normalized current (normalization to the peak currents at −20mV and 25 °C in the same cell) against membrane voltage (n = 3 for each group). (C) The activation and inactivation curve of the WT, p.I136V, p.I848T, and p.V1316A mutant channels at 15 °C are fitted with a Boltzmann function (n = 5 for each measurement). The sample sweeps are shown in part A. (D) The activation and inactivation curves of the WT and mutant channels at 40 °C are fitted with a Boltzmann function (n = 5 for each measurement). The sample sweeps are shown in part (A). (E) The area of window currents is obtained from part B and C for the WT and different mutant channels at 15 °C, 25 °C, and 40 °C, respectively (*p < 0.05 compared to 25 °C in the WT and mutant channels, respectively).