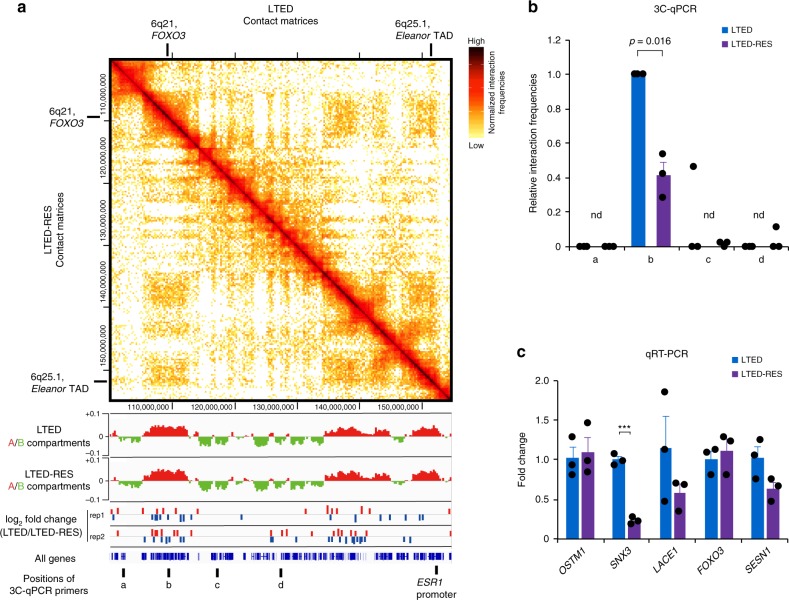
Fig. 3.
Resveratrol treatment reduced the interaction between ESR1 and FOXO3 but maintained the FOXO3 gene activity. a The resveratrol treatment affected the interaction between the Eleanor topologically associating domain and other A compartments. Top: Contact matrices from Hi-C, binned at 250-kb resolution. The normalized interaction frequencies of long-term estrogen deprivation (LTED) and LTED-RES cells are shown above and below the diagonal line, respectively. Middle: A/B compartments and fold changes in the contact frequencies. Positions of gained (red) and reduced (blue) contacts with the ESR1 promoter are shown. Bottom: Positions of all genes and 3C-qPCR (chromosome conformation capture–quantitative polymerase chain reaction) primers, as in Fig. 2a. b 3C-qPCR shows the relative interaction frequencies of the b site decreased by resveratrol treatment. c Relative expression levels of genes at 6q21 in LTED and LTED-RES cells. The LTED expression level was set to 1. Data presented in b, c are representative of three independent experiments (mean ± s.e.m.). P values were calculated using unpaired, two-tailed, Student’s t test (***P < 0.001, n.d. = not detected in at least one experiment)