Fig. 7.
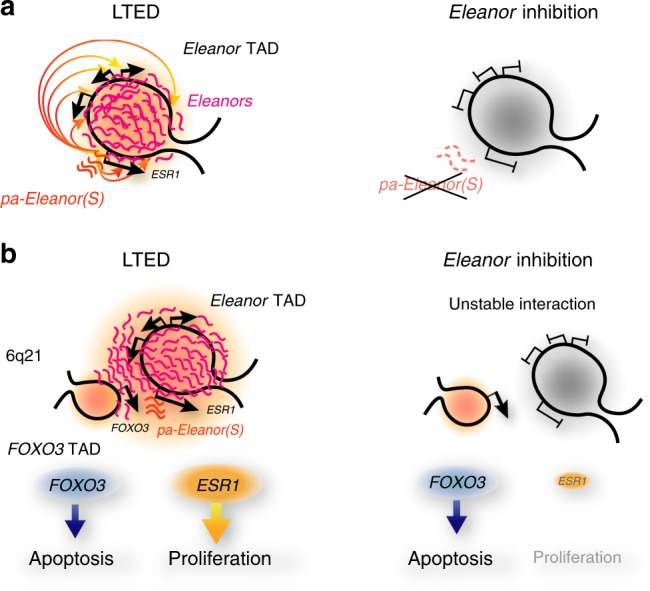
Proposed model of Eleanor functions in long-term estrogen deprivation (LTED) cells. Eleanors play roles in activating genes within the Eleanor topologically associating domain (TAD) (a) and in mediating the long-range chromatin interaction (b). a In LTED cells, pa-Eleanor(S) activates the transcription of Eleanors and RNA cloud formation, thus activating the genes in the Eleanor TAD, including ESR1 (left). Eleanor inhibition represses the Eleanor TAD (right). b In LTED cells, the gene for proliferation (ESR1) and the gene for apoptosis (FOXO3) are in close proximity, as both are active in the A compartment. Upon inhibition of Eleanors by resveratrol or pa-Eleanor(S) knockdown, the long-range chromatin interaction decreased and the ESR1 gene was repressed, but the FOXO3 gene activity was maintained at a high level. These suggest a mechanism underlying the apoptosis-prone nature of LTED cells
