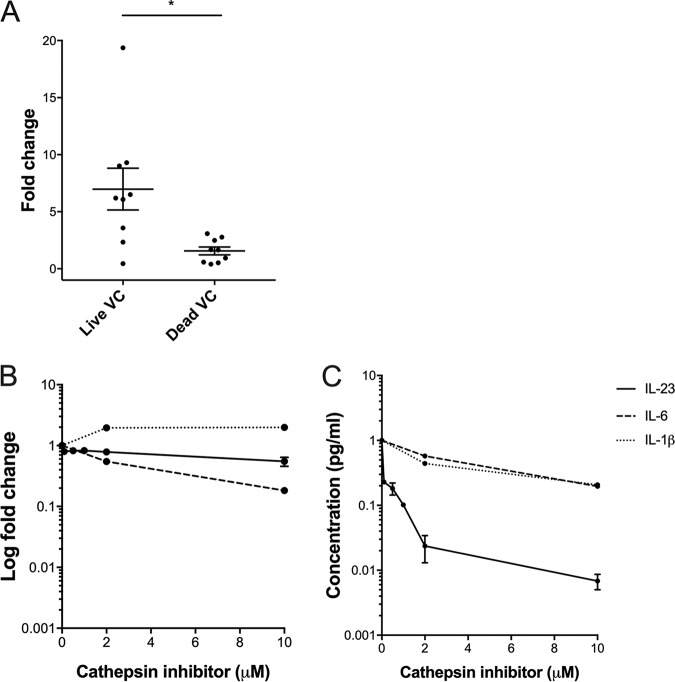
FIG 5.
Induction of inflammatory cytokines in response to stimulation of human THP-1 cells with wild-type V. cholerae in the presence of a cathepsin B inhibitor. (A) Cathepsin B expression (expressed as fold change) in THP-1 monocytes in response to live V. cholerae N16961 (Live VC) or heat-inactivated V. cholerae N16961 (Inactivated VC). Horizontal bars represent mean values across multiple biological replications of the cell culture stimulation experiment, and error bars represent standard errors of the means. *, P < 0.05 (by paired nonparametric testing). IL23A, IL6, and IL1β expression (B) and secretion (C) in THP-1 cells incubated with various concentrations of the cathepsin B inhibitor for 3 h and then exposed to live or heat-inactivated V. cholerae N16961 for 1 h. Expression was determined by qRT-PCR analysis of the IL23A, IL6, and IL1β genes, respectively, using cDNA from THP-1 cells. Expression levels were quantified relative to expression in an unstimulated control (medium) and expression of the housekeeping gene ACTB (β actin) using the ΔΔCT method of qRT-PCR analysis. Expression data are represented on a logarithmic scale (log2 ΔΔCT) , expressed as fold change. IL-23, IL-6, and IL-1β secretion from THP-1 cells was determined by ELISA using the THP-1 cell supernatant. Experiments were conducted in replicates of two, and error bars represent standard errors of the means.