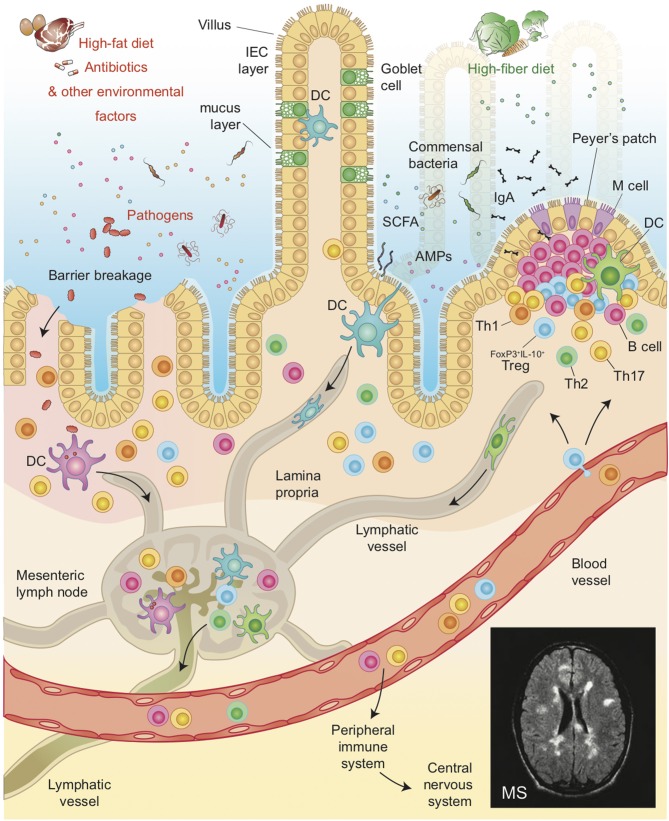
Figure 1.
Illustration of the host intestinal barrier, including the complex interaction among IEB, and mucus layer and its role in modulating the cross-talk between commensal bacteria and the GALT. Environmental factors such as diet, pathogens or antibiotics affect the pathogenesis of MS by altering gut microbiota composition, intestinal permeability and by favoring the translocation of bacteria or microbial products, thereby shaping auto-immune responses both in the gut and in peripheral organs such as the Central Nervous System in Multiple Sclerosis.