Figure 2.
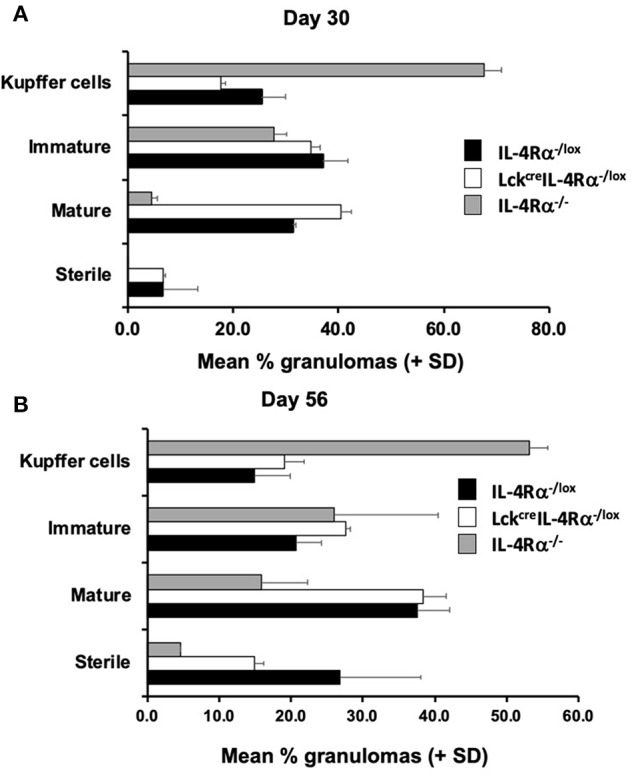
CD4+ T cell specific IL-4Rα−/lox (LckcreIL-4Rα−/lox), wild-type control (IL-4Rα−/lox), and global IL-4Rα−/− BALB/c mice were infected with L. donovani on day 0 post-infection and sacrificed at days 30 (A) and 56 (B) post-infection. At each time-point, sections of liver were removed, processed, and stained with haematoxylin and eosin to enable scoring of hepatic liver granulomas. Representative data from one of two experiments performed (n = 5/group). On day 30 (A) the distribution was significantly different for control and global IL-4Rα−/− mice (χ2 = 44; p < 0.00001) and CD4+ T cell specific IL-4Rα−/lox (LckcreIL-4Rα−/lox) and global IL-4Rα−/− mice (χ2 = 63; p < 0.00001). On day 56 (B) the distribution was significantly different for control and global IL-4Rα−/− mice (χ2 = 46; p < 0.00001) and CD4+ T cell specific IL-4Rα−/lox (LckcreIL-4Rα−/lox) and global IL-4Rα−/− mice (χ2 = 30; p < 0.00001).
