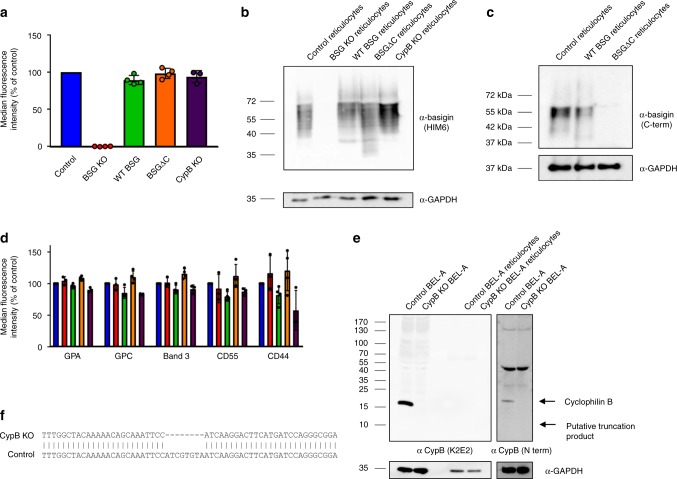
Fig. 4.
Lentiviral expression of exogenous basigin in BSG KO BEL-A cells allows for efficient rescue of receptor presentation in reticulocytes. a Bar graphs illustrating expression of basigin as assessed by flow cytometry on reticulocytes derived from indicated cell lines. Data are normalized to endogenous expression of basigin in reticulocytes derived from unedited BEL-A cells and depict the average median fluorescent intensity across four independent cultures (n = 4) or 3 (n = 3) in the case of CypB KO. Error bars represent standard deviation of the mean, and individual data points are represented as filled circles. b Immunoblots of basigin and GAPDH in reticulocytes derived from indicated BEL-A cell lines. c Immunoblot of basigin using C-terminal basigin antibody in reticulocytes derived from indicated BEL-A cell lines. d Bar graphs illustrating expression of reported malaria receptors on reticulocytes derived from indicated cell lines. Data are normalized to endogenous expression of each receptor in reticulocytes derived from unedited BEL-A cells and depict the average median fluorescent intensity across three or four independent cultures (n = 3 for BSG and CypB KO, n = 4 for WT and BSGDC). Error bars represent standard deviation of the mean, and individual data points are represented as black circles. e Immunoblots of lysates from undifferentiated control (unedited) and PPIB (CypB) knockout BEL-A cells and BEL-A-derived reticulocytes with anti-cyclophilin B and anti-GAPDH antibodies demonstrate absence of cyclophilin B (and putative truncation product) expression in PPIB CRISPR gene edited cells. f Sanger sequencing of PPIB gene in edited cells reveals a homozygous 8 base pair deletion at position 284 illustrated by sequence alignment that results in a frameshift. Source data are provided as a Source Data file