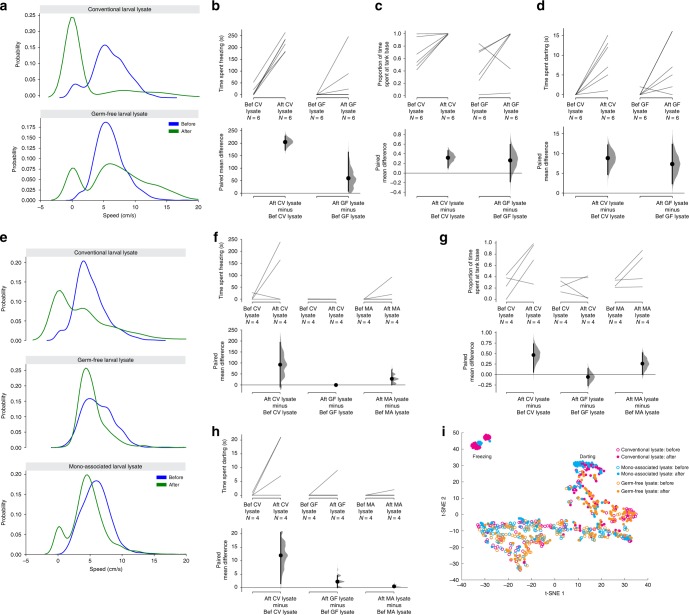
Fig. 6.
Fish and bacteria provide components of the alarm substance. Effect of lysate from conventional (CV) and germ-free (GF) larvae on behavior of adult zebrafish (n = 6 each), as shown by speed probability density function (a), and change in freezing (b), time spent at the tank base (c), and darting (d). e–h. Effect of lysate from a separate batch of conventional (CV), germ-free (GF), and monoassociated (MA) larvae on behavior of adult zebrafish (n = 4 each). i Swimming behavior was clustered using t-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding (t-SNE). Each data point represents behavior within a 5 s epoch. Filled circles indicate behavior that occurs after delivery of the lysate. The response to lysate from conventional is monoassociated larvae (blue and red circles) are more similar than the response to lysate from germ-free larvae (orange circles). The cluster on the top left corner corresponds to prolonged freezing behavior, which was not evoked by lysate from germ-free fish. Other postlysate clusters may represent darting behavior