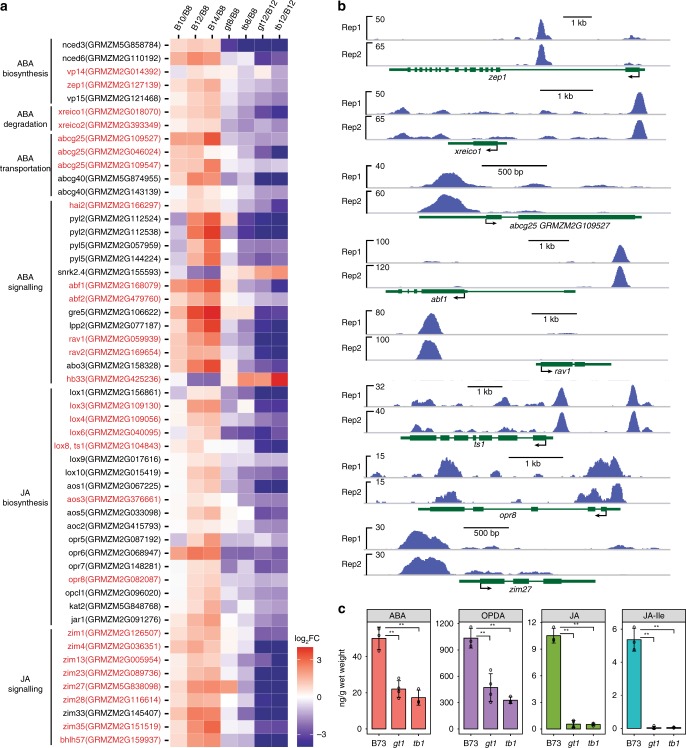
Fig. 3.
Bud dormancy is associated with tb1-gt1-mediated regulation of ABA and JA hormone homeostasis and signaling. a Genes involved in ABA biosynthesis, ABA degradation, ABA transportation, ABA signaling, JA biosynthesis and JA signaling were up-regulated in tiller buds across the B73 developmental series (B10/B8, B12/B8, B14/B8), but down-regulated in growing gt1 and tb1 buds. Stages and genotypes are indicated as described in Fig. 1, with slashes representing pairwise comparison between two samples (e.g. B10/B8 is a pairwise comparison between B73 buds at 10 vs. 8 DAP). Genes were highlighted in red if they were also putative direct targets of TB1 identified by ChIP-seq. FC fold change. Gradient color scale indicates the log value of expression fold change (log2FC). b TB1 ChIP-Seq-binding peaks near differentially expressed ABA and JA genes from (A). rep1 and rep2 represent two biological replicates of the TB1 ChIP-seq assay. c Quantification of ABA, OPDA, JA, and JA-Ile levels in tiller buds of B73, gt1, and tb1 at 12 DAP. OPDA 12-oxo-phytodienoic acid, JA-Ile Jasmonic acid-isoleucine. Data are means ± SE calculated from at least three biological replicates. **p < 0.01; two-tailed Student’s t-test