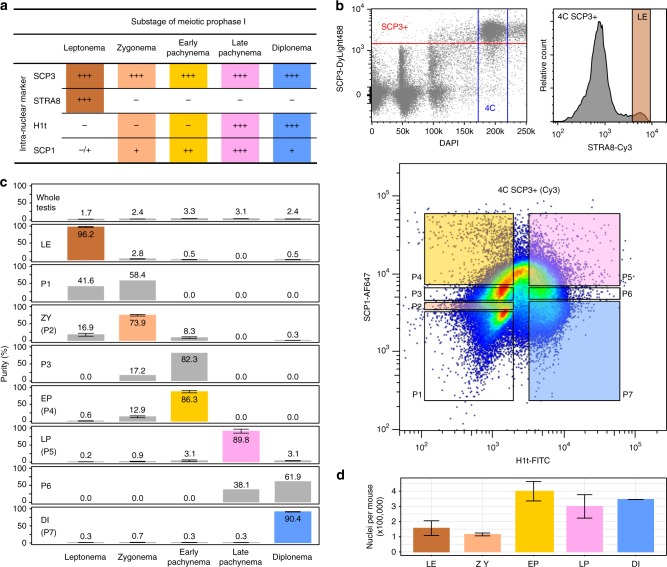
Fig. 2.
Experimental design for isolating stage-specific spermatocyte nuclei. a Signal strength of intra-nuclear markers across meiotic substages observed in immunofluorescence staining. Signal strength is classified as absent (−), very weak (−/+), weak (+), medium (++), or strong (+++). Combinatorial markers for isolating stage-specific nuclei are highlighted. b Flow cytometric strategies for isolating populations of stage-specific nuclei. Meiotic 4C nuclei are gated by DAPI and SCP3 signals (top left). Stage-specific nuclei are sorted into populations based on combinatorial signals of intra-nuclear markers in two separate sorts; one using antibodies against STRA8 for leptonema (top right), and the other one using antibodies against H1t and SCP1 for seven populations (P1 to P7) (bottom). c Distributions and purities of each specific type of nuclei in whole-testis and in sorted populations. The five selected populations of leptonema, zygonema, early pachynema, late pachynema, and diplonema are highlighted as LE, ZY, EP, LP, and DI, respectively. Purities (mean with standard error) of these populations are derived from two or three independent sorts. d Numbers of nuclei in each subpopulation collected in an adult mouse. Data (mean with standard error) are derived from two independent sorts. Source data are provided as a Source Data file