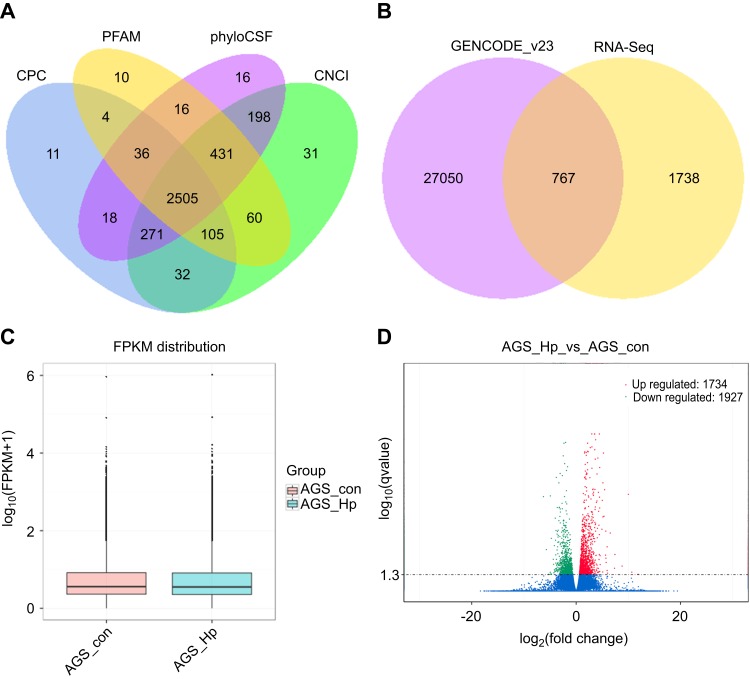
Figure 1.
LncRNA identification and differential expression analysis of the detected transcripts. (A) Four tools (CPC, CNCI, PFAM, and PhyloCSF) were employed to analyze the coding potential of candidate lncRNAs. (B) Venn diagram showing the distribution of the obtained lncRNAs in GENCODE_v23 and RNA-seq. (C) Box plots showing the FPKM distribution for all the detected transcripts. (D) Volcano plot of the significantly differentially expressed transcripts between H. pylori-infected and non-infected AGS cells (p-value<0.05).
Abbreviations: lncRNAs, long noncoding RNAs; CPC, coding potential calculator; CNCI, coding-non-coding-index; PhyloCSF, phylogenetic codon substitution frequency; FPKM, fragments per kilo-base of exon per million fragments mapped.