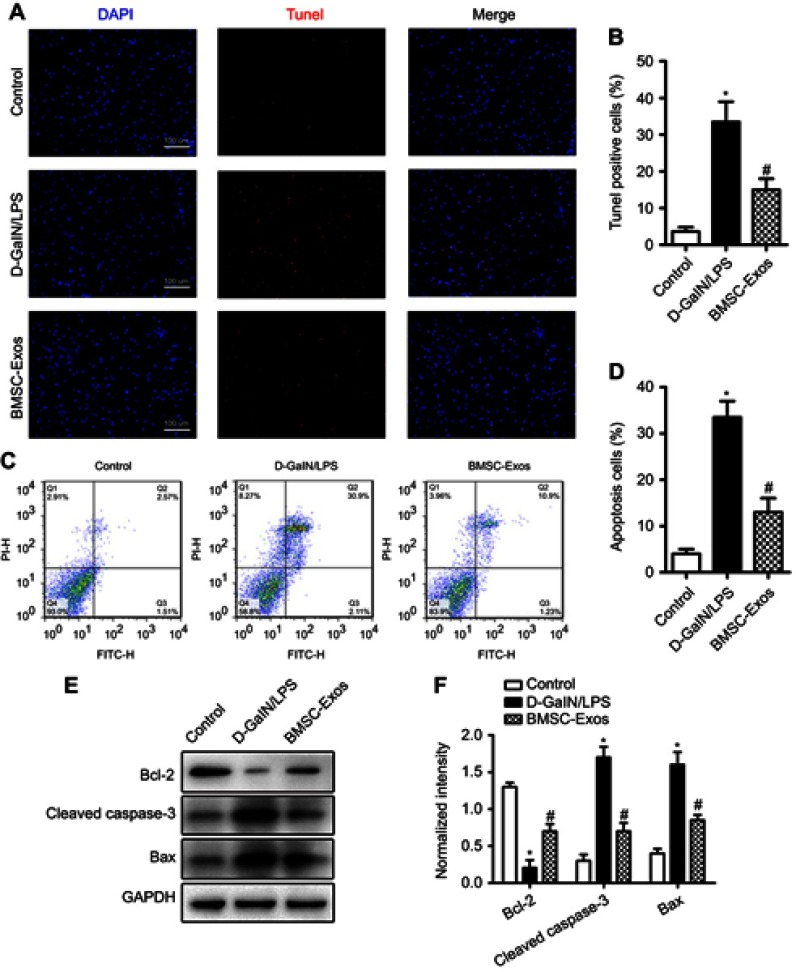
Figure 3.
BMSC-Exos pretreatment attenuates D-GaIN/LPS-induced hepatocyte apoptosis. (A) TUNEL-staining (red) for detection of apoptosis in hepatocytes. Cell nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). (B) Quantitative estimation of the proportion of apoptotic cells in each experimental group: control, D-GaIN/LPS, and BMSC-Exos pretreatment followed by D-GaIN/LPS as indicated (BMSC-Exos+D-GaIN/LPS). Pretreatment with BMSC-Exos substantially reduced D-GaIN/LPS-induced apoptosis. (C) Annexin V/FITC/PI double staining flow cytometry was also used to detect hepatocyte apoptosis induced by D-GaIN/LPS with or without BMSC-Exos pretreatment. (D) Quantitative results of flow cytometry confirming that BMSC-Exos pretreatment reduced D-GaIN/LPS-induced apoptosis of hepatic cells. (E) Western blot analysis of hepatocyte apoptosis-related proteins. (F) Relative expression levels of apoptosis-related proteins normalized to GAPDH. Pretreatment with BMSC-Exos upregulated anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 and downregulated pro-apoptotic Bax and cleaved caspase-3. *p<0.05 compared to the Control group, #p<0.05 compared to the D-GaIN/LPS group.
Abbreviations: BMSC-Exos, Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes; D-GaIN/LPS, D-galactosamine and lipopolysaccharide; Bax, Bcl-2-associated X protein; Bcl-2, B cell lymphoma 2; FITC, fluorescein isothiocyanate; PI, propidium iodide; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; TUNEL, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick end labeling assay.