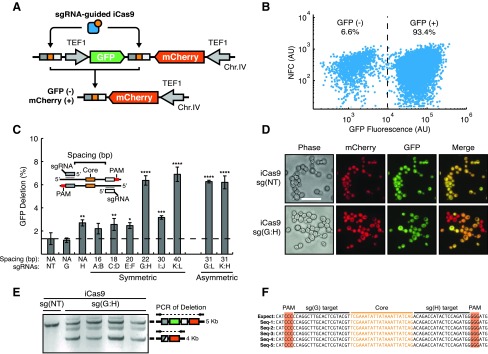
FIG. 2.
Validation of iCas9 function and target site design using a yeast-based GFP-deletion assay. (A) A diagram of chromosomally integrated dual-fluorescent reporter for detection of iCas9 function. The reporter contains GFP (green) and mCherry (red) coding regions transcribed from separate TEF1 promoters (gray arrows). iCas9 recognition sites flank the GFP expression cassette, wherein each site contains a left (dark gray rectangle) and right (light gray rectangle) protospacers flanking a TN3 Res1 core sequence (orange square). Functional targeting of iCas9 results in GFP deletion generating GFP−, mCherry+ cells. (B) A representative flow cytometry scatter plot for yeast expressing the reporter, iCas9, sgRNAs G and H after 96 h of galactose induction of iCas9 expression. NFC, nonfluorescent channel. (C) Systematic analysis of sgRNA spacing on iCas9 function, as measured by GFP deletion on flow cytometry. Inset shows spacing as measured from the 5′ ends of sgRNAs flanking the core sequence. sgRNAs A–M are systematically spaced around the core sequence and distances ranging from 16 to 40 bp. Nontarget sgRNA [sg(NT)] is a control guide not matching the target site, where the dashed line indicates background false GFP deletion. “Symmetric” indicates left and right guides are positioned equal distances around the core site. “Asymmetric” guide combinations are at varying distances from the core. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001 compared with sg(NT) by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett's multiple comparison test. (D) Fluorescent microscopy of yeast expressing iCas9 and sg(NT) or the 22 bp targeting pair, sg(G:H). GFP and mCherry dual-positive cells are orange on merge, while GFP deletions appear as red only (GFP−, mCherry+). Scale bar is 20 μm. (E) Gel electrophoresis of amplicons using primers flanking the reporter locus. The starting reporter results in a 5 kilobase (kb) PCR product and GFP deletion results in a 4 kb amplicon. Coexpression of iCas9 and sg(G:H) results in detectable DNA deletion via formation of the 4 kb product. (F) Sequencing of iCas9 target sites from isolated and subcloned deletion amplicons. Sequencing results (Seq1–Seq5) aligned to the expected recombination product (Expect). Deletion products match the expected recombination sequence and are free of insertion deletion (indel) mutations.