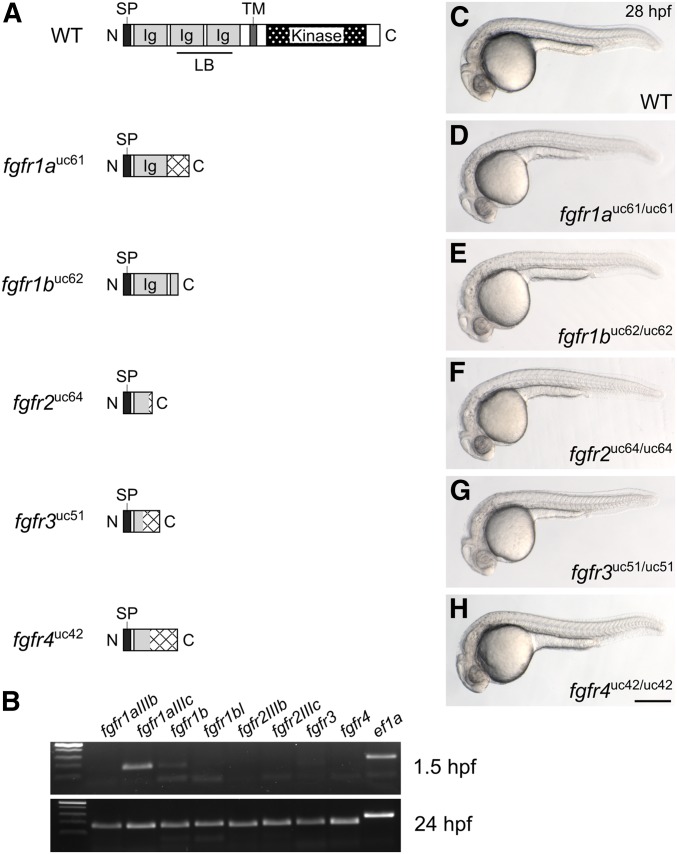
Figure 1.
Fgf receptor mutants are embryonic viable. (A) Schematic diagram of a typical full-length Fgfr protein and the predicted truncated peptides resulting from the fgfr1auc61, fgfr1buc62, fgfr2uc64, fgfr3uc51, and fgfr4uc42 alleles. Hatching indicates missense amino acids. (B) RT-PCR of wild-type embryos. While all fgfr isoforms are detected in 24 hr postfertilization (hpf) embryos (postzygotic genome activation, bottom panel), only fgfr1a (isoform IIIc) and fgfr1b are detected in 1.5 hpf embryos (prezygotic genome activation, top panel). ef1a is shown as a positive control. (C–H) Lateral view of ∼28 hpf wild-type (WT, C) or homozygous mutant (D–H) embryos. Anterior is to the left, dorsal is up. Bar in (H), 200 μm for (C–H). Ig, immunoglobulin; LB, ligand-binding domain; SP, signal peptide; TM, transmembrane domain.