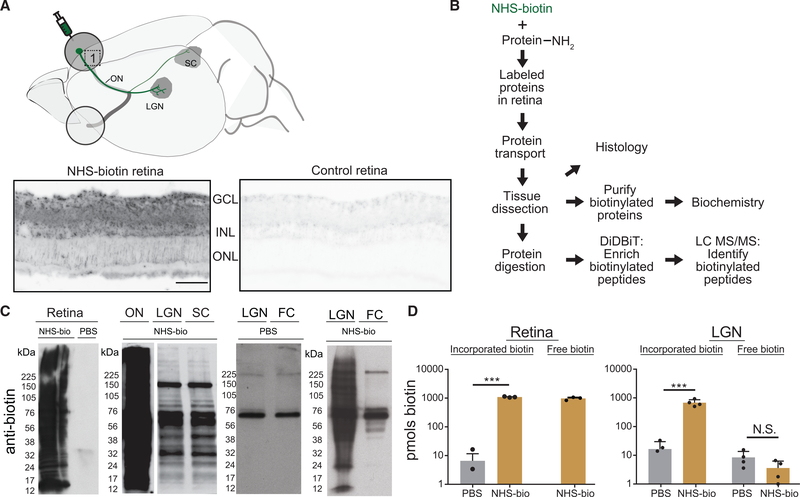
Figure 1. In Vivo Intravitreal NHS-Biotin Injection Labels Retinal Proteins Transported into the Visual Pathway.
(A) Diagram of the rat visual system schematizing the retinal injection of NHS-biotin and retinal ganglion cell projection sites from which transported biotinylated proteins were analyzed. Biotinylated proteins, visualized by tyramide signal amplification in retinal cross sections, were distributed throughout the retina but enriched in the ganglion cell layer (GCL) and inner nuclear layer (INL) in the NHS-biotin-injected tissue only. Images were collected under the same acquisition parameters. Scale bar = 25 μm and applies to both images.
(B) Workflow for in vivo protein labeling strategy and analysis of biotinylated proteins. Adult rats received intravitreal injections once a day for 7 days, and tissue was collected 11 days after the first injection. NHS-biotin binds irreversibly to amino groups of lysine residues and the N-terminals of proteins. Biotinylated proteins are either analyzed in histological sections or purified from brain regions and used for biochemical analysis or tandem MS (MS/MS). Biotin-labeled peptides are identified directly by MS/MS.
(C) Western blot detection of biotinylated proteins from retina, ON, LGN, SC, and the non-visual area, the frontal cortex (FC), following in vivo intravitreal injection of NHS-biotin or saline. Asterisks mark endogenously biotinylated carboxylases at ~60 and 120 kDa, the only labeled proteins in the FC.
(D) Comparison of biotin incorporated into proteins from retina (left) and LGN (right) and free biotin from LGN (right) after intravitreal NHS-biotin or phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) injections. Significantly more biotin was bound to protein in NHS-biotin samples compared with background values in PBS. In LGN samples, significantly more biotin was bound to protein in animals with intravitreal NHS-biotin injections compared with PBS. Comparable low levels of free biotin were detected in LGN from NHS-biotin- and PBS-injected animals, indicating that most biotin in LGN samples was bound to the protein.
Retina, n = 3, ***p < 0.001, two-tailed Student’s t test; LGN, n = 4, ***p < 0.001, two-tailed Holm-Sidak corrected t test. Means ± SEM.