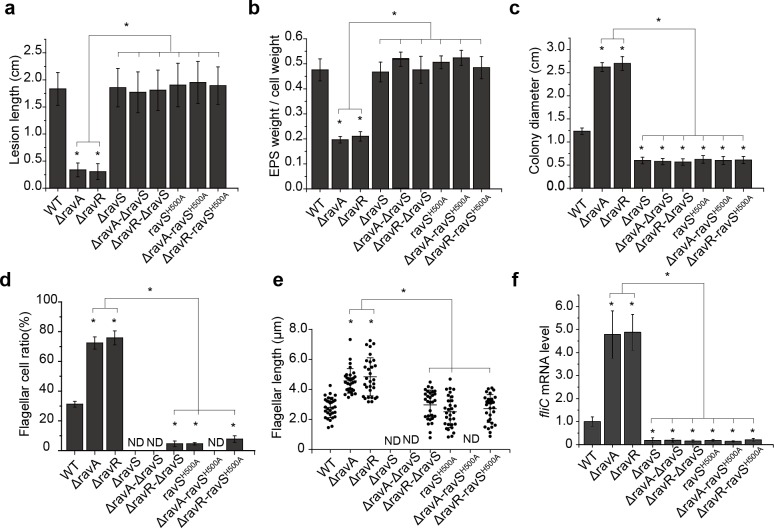
Fig 3. Epistatic analysis revealed that ravS is downstream of ravA-ravR in regulation.
(a–f) Deletion of ravS or the ravSH500A point mutation effectively suppressed the phenotypic deficiencies of X. campestris pv. campestris caused by ravA or ravR mutations. (a) Bacterial virulence measured by the lesion length on leaves. Bacterial strains were inoculated onto plant leaves of Brassica oleracea cv Zhonggan 11. The lesion length was recorded 10 d after inoculation (n = 30). (b) Production of extracellular polysaccharides (EPS). EPS production was quantified as the ratio of dry weight of EPS vs. the dry weight of bacterial cells (n = 3). (c) Bacterial swimming motility measured by the diameters of swimming zones. Bacterial strains were inoculated in NYG plates containing 0.15% agar and grown at 28°C for 28 h. The average diameters of the migration zones were measured (n = 10). (d) Ratio of bacterial cells with flagella. For each strain, cells with flagella were counted (n = 100). (e) The average flagellar length of bacterial strains (n = 30). (f) fliC mRNA levels in bacterial strains. The level of fliC mRNA was measured by qRT-PCR. Amplification of cDNA from tmRNA was used as an internal control. The experiment was repeated three times and the result of a representative experiment is shown. In (a–f), standard deviations are provided; asterisk: significant difference, as tested by Student’s t-test (P ≤ 0.05).