Figure 3-. Aptamer target binding is inhibited in the presence of anti-PEG antibody.
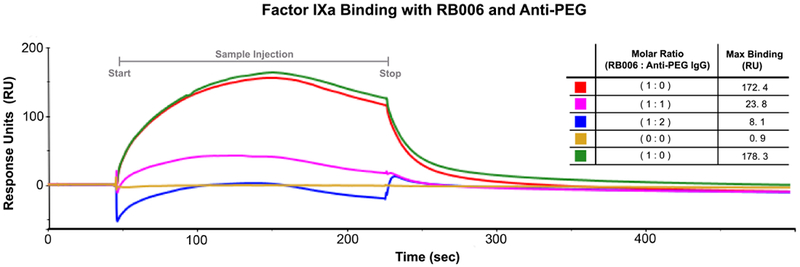
Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) was used to test the binding of RB006 to its target protein FIXa both alone and in the presence of anti-PEG IgG. Factor IXa was covalently attached to the chip surface and binding was measured in Response Units (RU) after injection of either RB006 alone (red and green, replicates) or RB006 in the presence of increasing molar ratios of monoclonal anti-PEG antibody (pink and blue respectively). Data represent a single experiment, though the effect was reproducible in two other replicate experiments. (Inset) A decrease in max binding (RU) was observed when aptamer and antibody were premixed and injected over the surface of the chip. The order of listed samples reflects the order of sample injections. The chip surface was uncompromised throughout the duration of the experiment as a similar Rmax was seen with the aptamer only samples injected at the beginning of the assay (red) and at the end of the assay (green).
