Figure 5-. Anticoagulant aptamer activity is inhibited in the presence of anti-PEG antibodies in vivo.
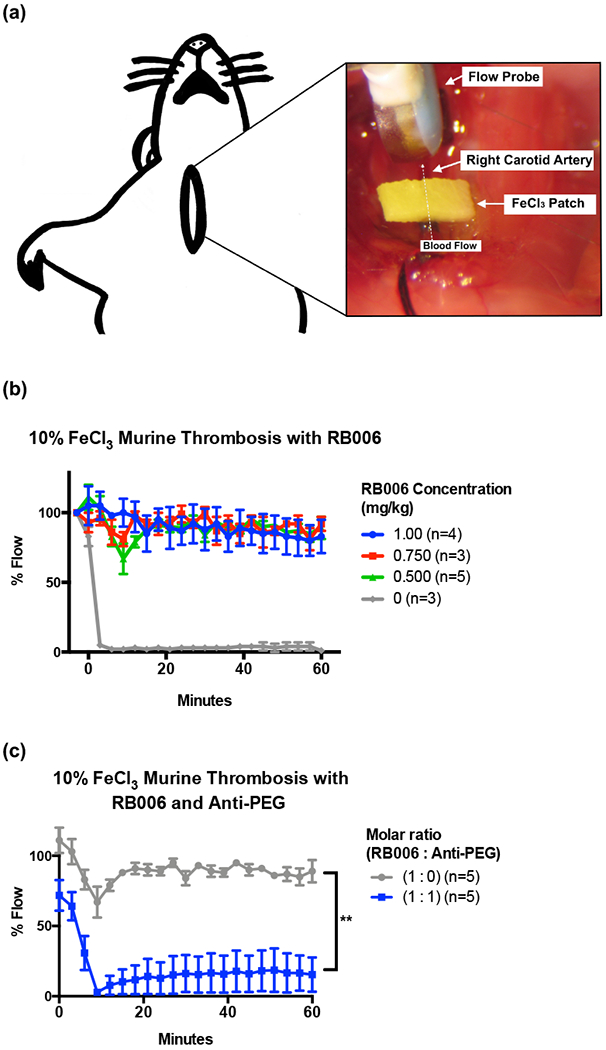
(a) Schematic represents the murine model of thrombosis used to analyze the antithrombotic / anticoagulant properties of aptamers and anti-PEG antibodies in real time. A ferric chloride (FeCl3) patch is used to induce endothelial damage to the carotid artery, and blood flow through the artery is measured via a distal flow probe. Percent blood flow at various time points post-intravenous (IV) administration of the aptamer was normalized to the blood flow prior to placement of the FeCl3 patch, with time zero indicating the time of patch removal.
(b) Increasing concentrations of PEGylated RB006 (green, red, blue) demonstrate the antithrombotic activity compared to buffer control (grey) in the murine model of thrombosis. Data represent the mean ± SEM of technical replicates as described in the figure legend.
(c) Addition of anti-PEG IgG at a 1:1 molar ratio to the PEGylated RB006 (blue) diminishes vessel patency in the murine thrombosis model as shown by a decrease in % Flow compared to aptamer alone (grey). For both treatment groups, RB006 was used at a concentration of 0.5 mg/kg. Data represent the mean ± SEM of technical replicates as described. **indicates p-value <0.01, using 2-way ANOVA vs. aptamer alone (1:0).
