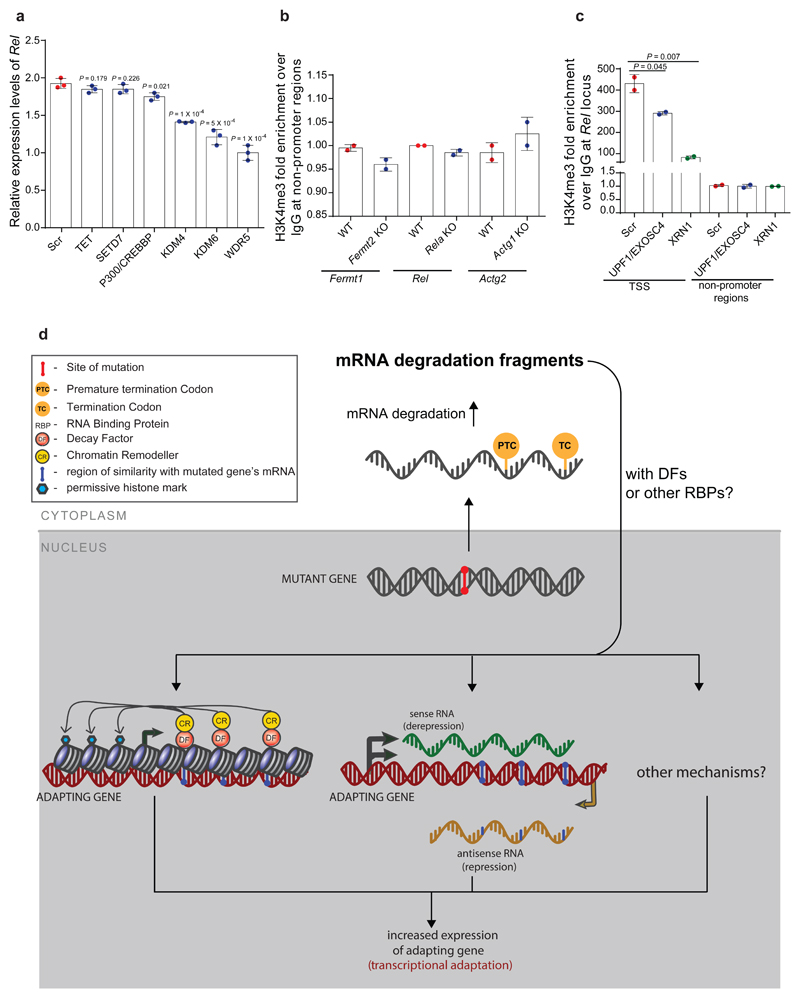
Extended Data Figure 9. Transcriptional adaptation involves chromatin remodeling dependent on decay factor activity.
a, qPCR analysis of Rel mRNA levels after siRNA mediated knockdown of the indicated proteins in Rela K.O. cells. b, ChIP-qPCR analysis of H3K4me3 occupancy at non-promoter regions (as a control) of Fermt1, Rel and Actg2 in Fermt-2, Rela and Actg1 K.O. cells, respectively, compared to wt. c, ChIP-qPCR analysis of H3K4me3 occupancy near the Rel TSS and a non-promoter region (as a control) after siRNA mediated knockdown of the indicated proteins in Rela K.O. cells. Scr: Scrambled siRNA control. d, Current expanded model of transcriptional adaptation to mutations. RNA decay fragments may act as intermediates to bring decay factors, and chromatin remodelers, to adapting gene loci, thereby triggering increased gene expression. Alternatively, RNA decay fragments may function to repress antisense RNAs at the adapting gene loci allowing for increased sense mRNA expression. It is, however, likely that additional mechanisms are involved in transcriptional adaptation, and possibly in a gene-dependent manner. a-c, n = 3 (a); 2 (b, c) biologically independent samples. Error bars, mean, s.d. Two-tailed student’s t-test used to assess P values.