Figure 5. Knockout of AhR in HSCs sensitizes mice to liver fibrosis and abolishes the anti-fibrotic activity of ITE.
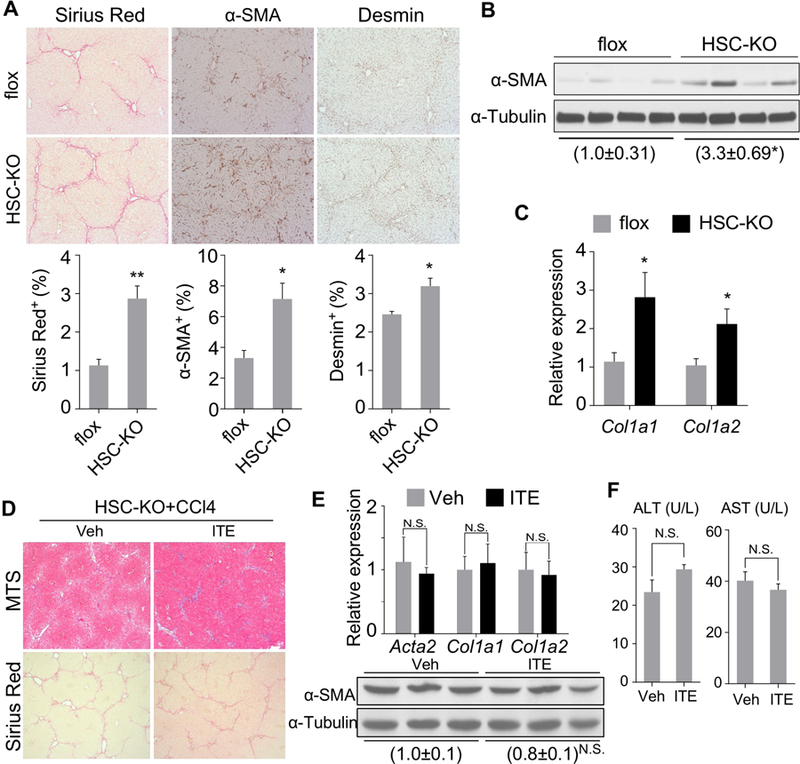
(A-C) 9–10 week old male AhRflox/flox (flox) and HSC-KO mice were treated with CCl4 (1 µl/g body weight) twice a week for 4 weeks (n=5 per group). The liver histology was analyzed by Sirius Red staining and immunostaining of α-SMA and Desmin (A, original magnification 10X with the quantifications of staining shown on the bottom). The α-SMA protein level was determined by Western blotting (B), and the mRNA expression of Col1a1 and Col1a2 was determined by real-time PCR (C). (D-F) 8–10 week old male HSC-KO mice were treated with vehicle or ITE (10 mg/kg) together with CCl4 (0.5 µl/g body weight) three times a week for four weeks (n=3 per group). Liver tissues were analyzed for histology by Masson’s Trichrome (MTS) and Sirius Red staining (D, original magnification 5X), the expression of fibrogenic gene by real-time PCR (top) or Western blotting (bottom) (E), and the serum ALT and AST levels (F). All data were presented as mean ± SEM. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01; N.S., statistically not significant.
