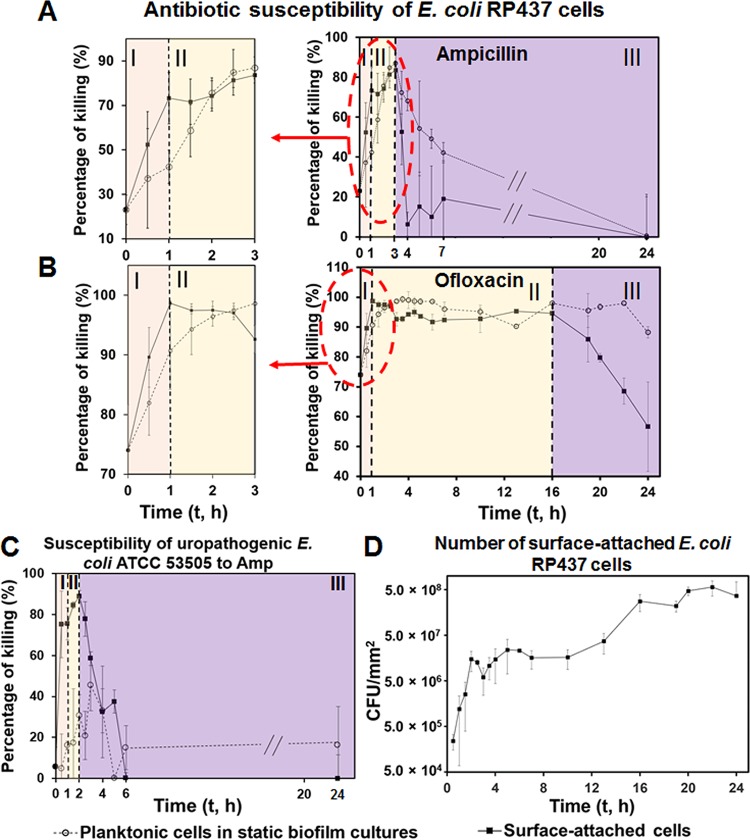
FIG 1.
E. coli antibiotic susceptibility during early stages of biofilm formation. (A and B) Reduction of surface-attached E. coli RP437 cells by 1-h treatment with 200-μg/ml Amp (A) or 10-μg/ml Ofx (B). (C) Reduction of surface-attached uropathogenic E. coli ATCC 53505 cells by 1-h treatment with 200-μg/ml Amp. (D) Number of surface-attached E. coli RP437 cells on glass surfaces. Dotted lines indicate the time points when major changes in antibiotic susceptibility occurred, which correspond to the three phases (I, II, and III) marked in panels A, B, and C. E. coli biofilms were formed on glass surfaces. The antibiotic susceptibility was tested in 0.85% NaCl solution (no carbon source) to minimize the effects of cell growth. At least five biological replicates were tested for each data point.