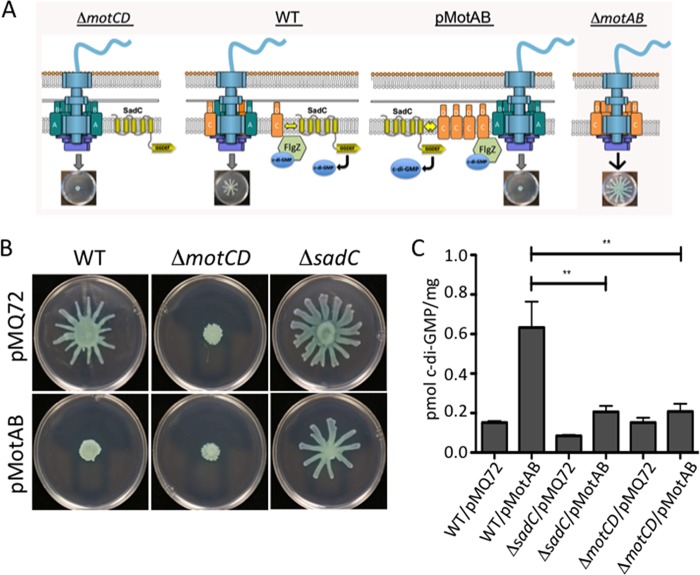
FIG 7.
MotAB-MotCD dynamics impact c-di-GMP levels. (A) Shown is a model of the flagellar motor with various configurations of the stators, including a ΔmotCD mutant (left), the wild type (center, left), a strain expressing MotAB from a multicopy plasmid (center, right), and the ΔmotAB mutant (left). Also shown is the c-di-GMP effector FlgZ, which can interact with MotC when FlgZ is in the c-di-GMP-bound state. A, B, C, and D refer to MotA, MotB, MotC and MotD, respectively. (B) Swarming motility as assessed for the indicated strains. (C) c-di-GMP quantification assays. Data are expressed as picomoles of c-di-GMP per milligram (dry weight) of cells from which nucleotides were extracted. Values are means ± SEM. Significance was determined by analysis of variance and Dunnett’s posttest comparison to the WT carrying the vector plasmid (pMQ72). **, P < 0.01.