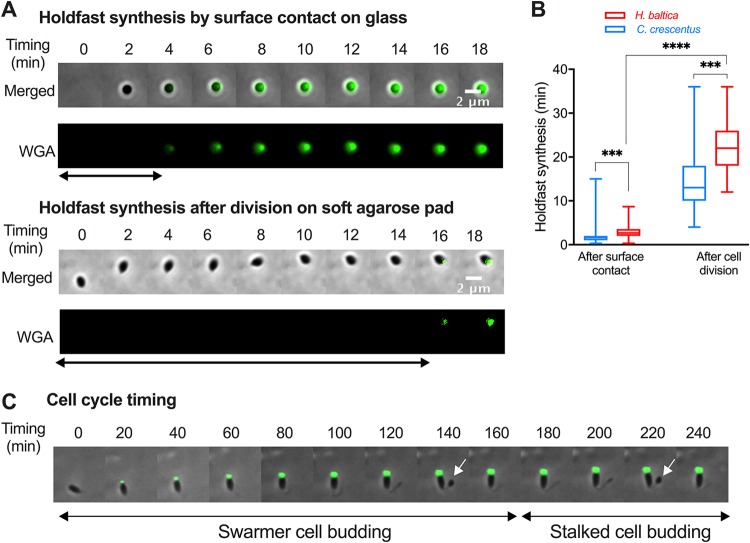
FIG 5.
H. baltica holdfast synthesis is regulated by a developmental pathway and in response to surface contact. (A) Montages of H. baltica holdfast synthesis by a newly budded swarmer cell on a glass surface on a microfluidic device (top) and on soft agarose pads (bottom). The holdfasts were labeled with WGA-AF488 (green). Images shown were acquired every 2 min, and holdfast synthesis timing was processed using MicrobeJ. The arrows indicate the time it took for holdfasts to be detected after surface contact. (B) Box-and-whisker plots representing the quantification of H. baltica holdfast timing via surface contact stimulation and developmental pathways. The data for C. crescentus holdfast synthesis timing were extracted from reference 44. The total number of cells analyzed was 100 for each setup. The variance between H. baltica and C. crescentus holdfast synthesis times was analyzed using a t test. ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001. (C) Time-lapse montage of an H. baltica swarmer cell differentiating into a budding stalked cell on an agarose pad containing WGA-AF488 to label the holdfast. Images were collected every 5 min for 3 h. The arrows point to incipient swarmer cells in predivisional cells.