Figure 2.
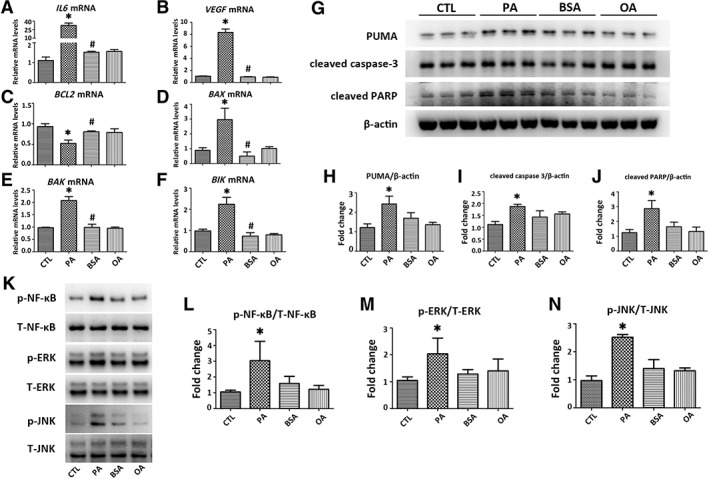
PA induces inflammation and apoptosis in HK‐2 cells. HK‐2 cells were exposed to PA (500 μM) or OA (500 μM) for 24 hours. Transcripts of (A, B) inflammatory and (C–F) apoptotic mediators including IL6, VEGF, BCL2, BAX, BAK, and BIK in HK‐2 cells were determined by qPCR. Results are expressed as fold change relative to CTL. (G): Representative Western blots of apoptotic mediators including PUMA, cleaved caspsae‐3, and cleaved PARP are presented, with (H–J) results after quantification of each protein normalized to β‐actin. (K): Representative Western blots of p‐NF‐κB, T‐NF‐κB, p‐ERK, T‐ERK, p‐JNK, and T‐JNK are presented, with (L–N) results after quantification of each phosphorylated protein normalized to total protein. All the ratios are then normalized with the ratio of CTL. Results are expressed as mean ± SD. Experiments were performed in triplicate. *, p < .05 versus CTL group; #, p < .05 versus PA group. Abbreviations: BAK, Bcl‐2‐antagonist killer; BAX, BCL‐2‐associated X protein; BCL2, B‐cell lymphoma 2; BIK, Bcl‐2‐interacting killer; BSA, bovine serum albumin; CTL, plain culture medium treated control cells; IL6, interleukin 6; OA, oleic acid; p‐ERK, phosphorylated extracellular signal‐regulated kinase; p‐JNK, phosphorylated c‐Jun N‐terminal kinase; p‐NF‐κB, phosphorylated nuclear factor‐κB; PA, palmitic acid; PARP, poly adenosine diphosphate ribose polymerase; PUMA, p53 upregulated modulator of apoptosis; qPCR, quantitative real‐time PCR; T‐ERK, total extracellular signal‐regulated kinase; T‐JNK, total c‐Jun N‐terminal kinase; T‐NF‐κB, total nuclear factor‐κB; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.
