Figure 4.
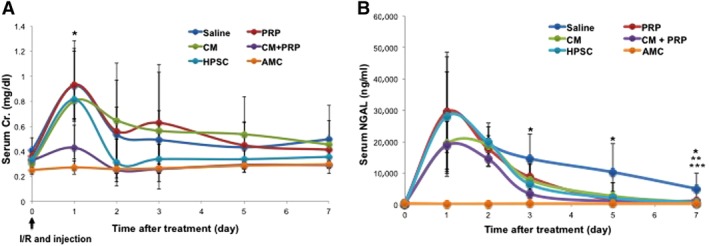
Functional improvement by injection of HPSC‐CM encapsulated with PRP in rats after ischemia/reperfusion (I/R). (A): Serum Cr levels in the CM with PRP group (CM + PRP) were significantly lower than in saline‐treated, PRP‐only‐treated, and CM‐only‐treated groups at 1 day post‐I/R (analysis of variance, Tukey test, *p < .05, CM + PRP vs. saline, PRP only, and CM only, n = 3–6). Although similar elevations in serum NGAL levels were observed, renal function improved the most in the CM + PRP group, based on lower serum NGAL levels than in the saline group at 3, 5, and 7 days (*, Tukey test at p < .05, CM + PRP vs. saline). (B): NGAL levels in the CM only and HPSC group also significantly decreased, compared with the saline group at 7 days (Tukey test at p < .05; **, CM vs. saline; ***, HPSC vs. saline). Data presented as mean ± SD (n = 3–6 per experimental group). Abbreviations: AMC, age‐matched control; CM, conditioned medium; HPSC, human placental stem cell; NGAL, neutrophil gelatinase‐associated lipocalin; PRP, platelet‐rich plasma.
