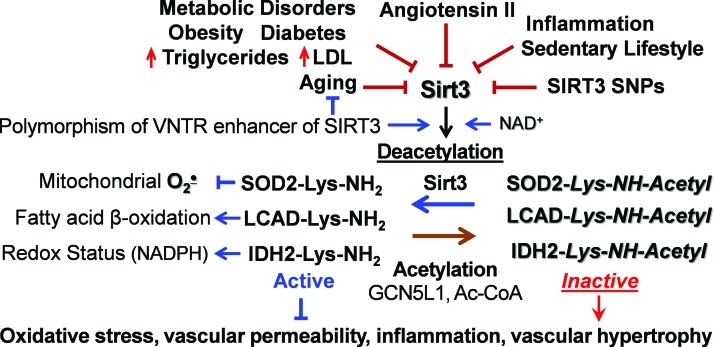
FIG. 1.
Multiple risk factors downregulate Sirt3, leading to mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress. Sirt3 depletion causes mitochondrial hyperacetylation due to imbalance between acetylation and deacetylation pathways. This leads to SOD2 inactivation, inhibition of fatty acid β-oxidation, and altered redox status due to inactivation of SOD2, LCAD, and IDH2, which contribute to vascular dysfunction and hypertension. IDH2, isocitrate dehydrogenase 2; LCAD, long-chain acyl coenzyme A dehydrogenase; Sirt3, mitochondrial deacetylase Sirtuin 3; SOD2, mitochondrial manganese superoxide dismutase. Color images are available online.