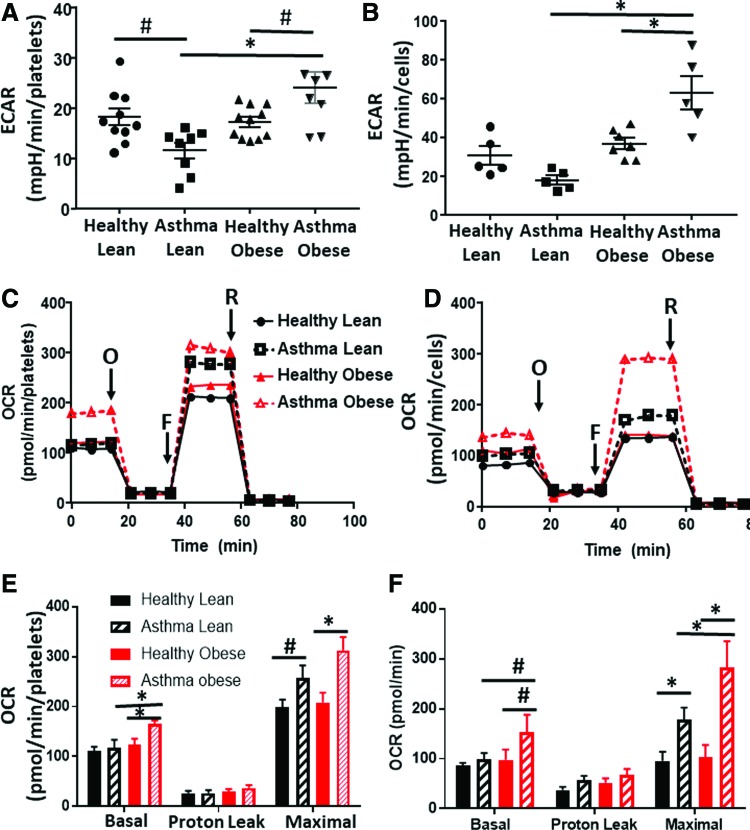
FIG. 1.
Platelet and airway epithelial cell bioenergetics differs in lean and obese asthmatics. (A, B) Measured basal ECAR of (A) platelets and (B) airway epithelial cells isolated from healthy lean, asthmatic lean, healthy obese, and asthmatic obese individuals. (C, D) Representative oxygen consumption traces of (C) platelets and (D) airway epithelial cells from all four experimental groups. Basal respiration rate was measured followed by proton leak after the addition of oligomycin (O), maximal respiration after the addition of FCCP (F), and nonmitochondrial respiration after the addition of rotenone (R). (E, F) Quantification of several traces in (E) platelets and (F) epithelial cells such as those shown in (C, D), respectively. For platelet studies: healthy lean (n = 10), lean asthmatic (n = 8), healthy obese (n = 11), and asthmatic obese (n = 8). For airway epithelial cells: all groups n = 5. All data are mean ± SEM. Statistical significance was tested by one-way ANOVA. #p < 0.05; *p < 0.01. ECAR, extracellular acidification rate; FCCP, carbonyl cyanide-ρ-trifluoromethoxyphenylhydrazone; SEM, standard error of the mean. Color images are available online.