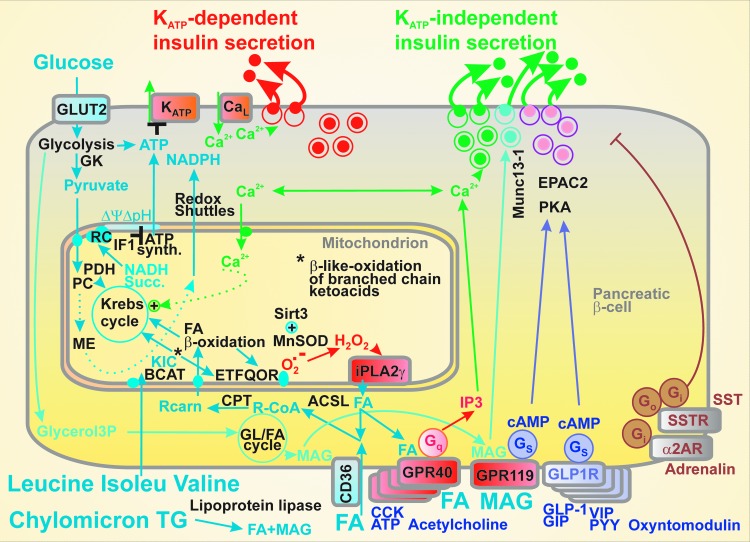
FIG. 2.
Mechanisms of insulin secretion. Emphasizing the KATP-dependent and KATP-independent pathways, which are interrelated namely by Ca2+ homeostasis, the scheme illustrates major metabolic and receptor-mediated pathways of insulin secretion, including the inhibitory pathways of α2-adrenergic and somatostatin (SST) receptors (α2AR, SSTR), respectively. GPRs for amino acids were not illustrated for simplicity. ASCL, long-chain acyl-CoA synthetases; BCAT, branched chain ketoacid aminotransferase; CCK, cholesystokinin; CPT, carnitine palmitoyl transferase; FA, (free) fatty acids; GK, glucokinase; GLUT2, glucose transporter 2; GPRs, G-protein-coupled receptors; KATP, ATP-sensitive K+ channel; KIC, 2-ketoisocaproate; MAG, monoacylglycerol; PC, pyruvate carboxylase; PKA, protein kinase A; PYY, peptide Y; RC, respiratory chain; VIP, vasoactive intestinal peptide.