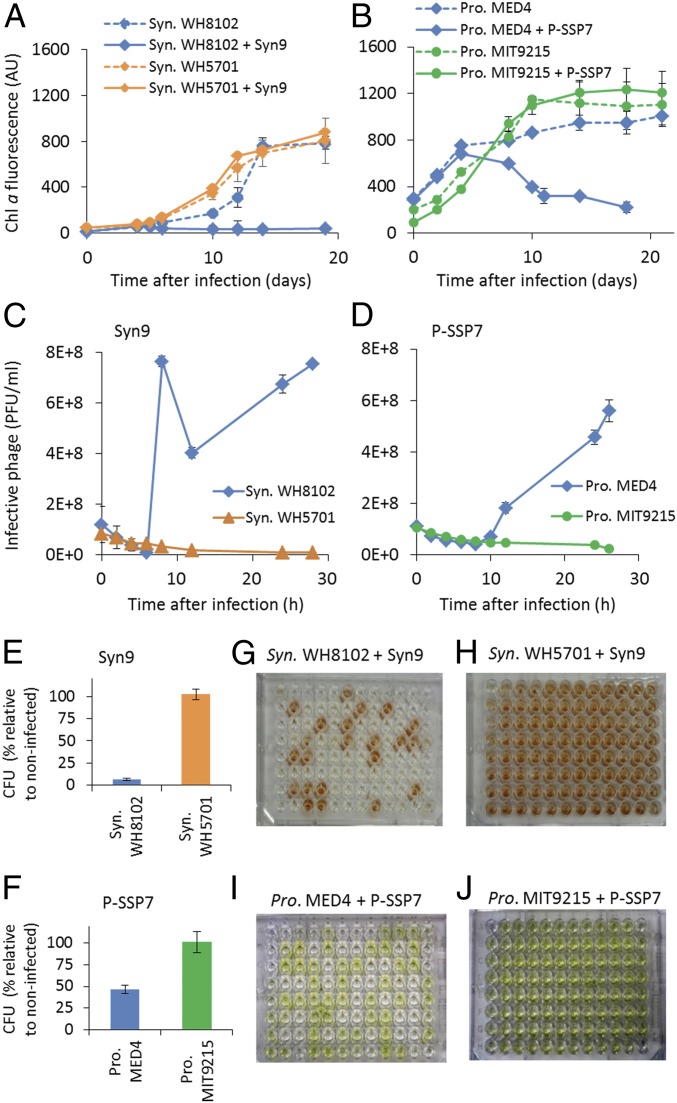
Fig. 1.
Determination of cyanobacterial resistance. Growth of cyanobacteria in the presence and absence of cyanophages (n = 6) (A and B) and production of infective cyanophages (n = 3) (C and D). These figures are representative of resistance and sensitivity for all interactions. Synechococcus (Syn.) WH8102 and Prochlorococcus (Pro.) MED4 are sensitive to the Syn9 and P-SSP7 phages, respectively, as seen by the decline in culture growth (A and B) and production of infective viral particles (C and D), whereas Syn. WH5701 and Pro. MIT9215 are resistant to these same cyanophages, respectively, as growth is unaffected by the cyanophages (A and B) and no infective particles were produced (C and D). Viable colony (E and F) and cell lysis (G–J) assays showed that all Syn. WH5701 and Pro. MIT9215 cells were resistant to Syn9 and P-SSP7, respectively (n = 3 for both assays, with a total of 576 cells analyzed in the cell lysis assay per interaction); Syn9 lysed 72% of sensitive Syn. WH8102 cells (G), and P-SSP7 lysed 52% of sensitive Pro. MED4 cells (I), while both phages lysed 0% of the respective resistant cells: Syn. WH5701 (H) and Pro. MIT9215 (J). AU, arbitrary units; Chl a, Chlorophyll a; CFU, colony-forming units; PFU, plaque-forming units.