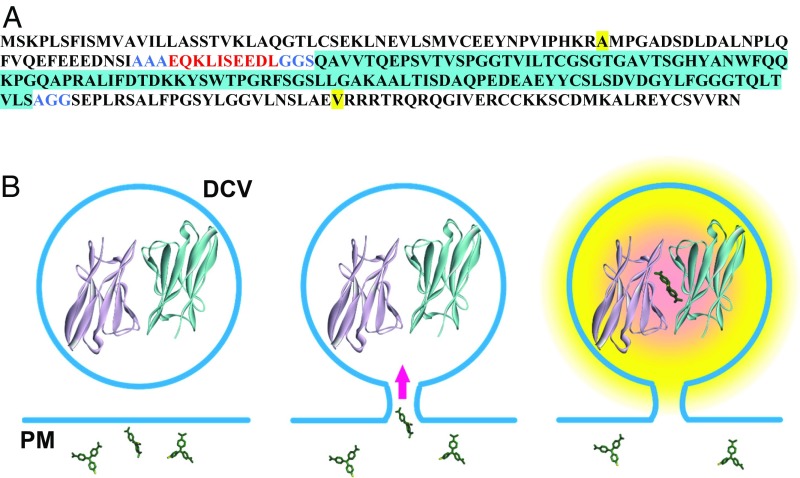
Fig. 1.
Design of Dilp2-FAP. (A) Amino acid sequence of Dilp2-FAP. Dilp2 sequence is shown in plain black with the beginning and end of the C-peptide (from uniprot.org) highlighted in yellow. The c-Myc tag is red, linker sequences (AAA, GGS, and AGG) are blue, and the FAP monomer inserted in the C-peptide is black with blue highlighting. (B) Schematic of FAP experiments. Left, fusion with Dilp2 ensures that FAP will be highly concentrated in DCVs so that dimerization can occur (structure from 8). Extracellular MG molecules are shown at different orientations. Center, formation of a fusion pore with the plasma membrane (PM) allows extracellular membrane impermeant MG derivatives to enter the DCV lumen. Right, formation of complex between the nonfluorescent FAP dimer and MG derivative produces fluorescence. Note that small MG derivatives will diffuse through the fusion pore to increase fluorescence more quickly than exit of large MG-liganded FAP dimers and higher order MG-liganded Dilp2-FAP complexes.