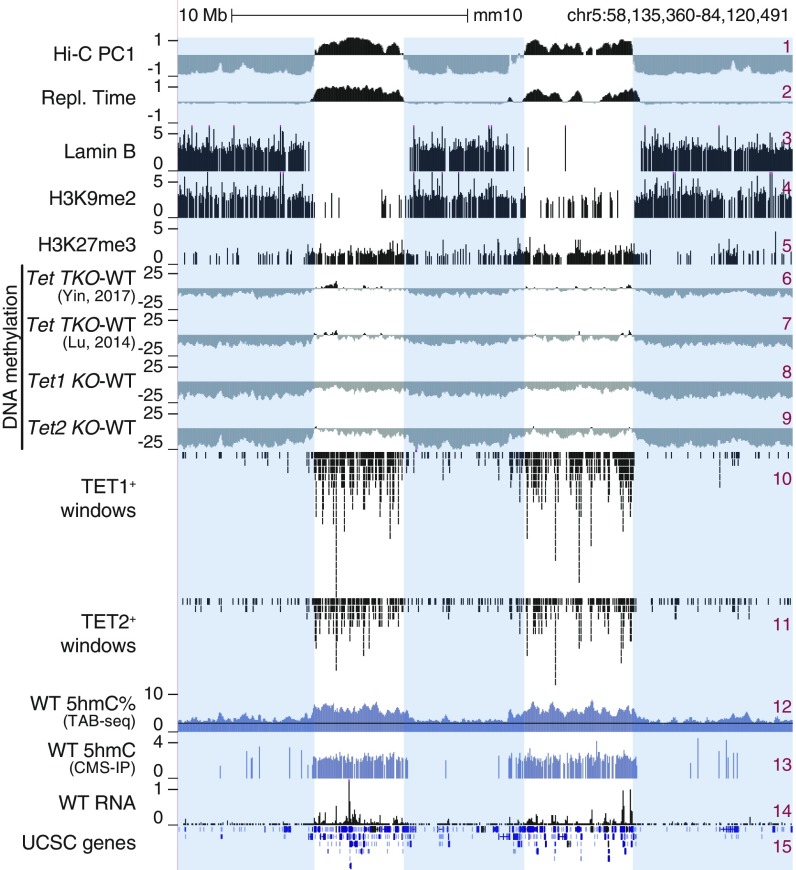
Fig. 2.
DNA hypomethylation in heterochromatin compartment in TET-deficient mESCs. Genome tracks showing an overlap between Hi-C-defined A/B compartments (track 1), early/late replicating sites (early replicating: positive values; track 2), lamina-associated domains (track 3), regions marked by histone marks H3K9me2 (track 4) and H3K27me3 (track 5), and large hypomethylated domains in different Tet KO mESCs (shown as subtraction of DNA methylation percentage, mutant minus WT; tracks 6–9). TET1 and TET2 binding (ChIP-seq; tracks 10–11), 5hmC distribution (TAB-seq and CMS-IP; tracks 12–13), and gene expression (RNA-seq; tracks 14) in WT mESCs are shown for reference. Heterochromatic Hi-C B compartment regions are highlighted.