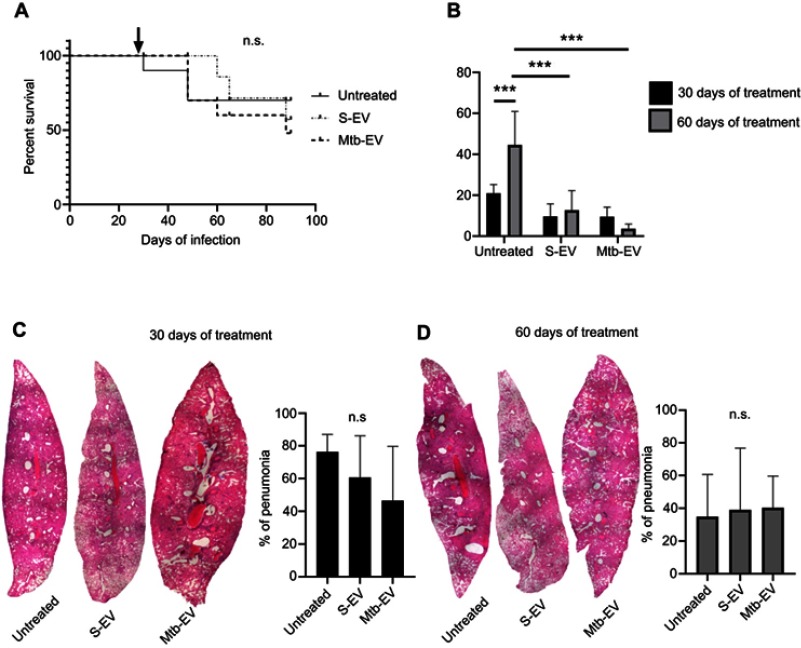
Figure 4.
EVs released by J774A.1 macrophages reduce the bacterial load in a mouse model of pulmonary tuberculosis. BALB/c mice were inoculated intra-tracheally with 2.5×105 CFU of M. tuberculosis H37Rv. Thirty days after infection, each mouse (10 mice per group) received intra-peritoneal injections (three times per week) of saline solution, alone, with EVs purified from J774A.1 cells (S-EV) or with EVs purified from J774A.1 cells that had been infected with M. tuberculosis H37Rv for 4 h (Mtb-EV). Mice lungs were analyzed after 30 or 60 days of treatment. (A) Mice survival. The arrow indicates the beginning of the indicated treatments. (B) Lung bacterial load. The graph represents mean and SEM of one experiment (representative of three independent experiments). Two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s test: ***p<0.001. (C) Lung sections and lung pneumonic areas at 30 days of treatment. The graph represents mean and SEM of one experiment (representative of three independent experiments). Kruskal–Wallis test: n.s., not significant. (D) Lung sections and lung pneumonic are at 60 days of treatment. The graph represents mean and SEM of one experiment (representative of three independent experiments). Kruskal–Wallis test.
Abbreviations: M. tuberculosis, Mycobacerium tuberculosis; CFU, colony forming unit; EVs, extracellular vesicles; SD, standard deviation; n.s., not significant.