Figure 7: DHA decreased CCI-induced CD68 activation in cortex at PID3.
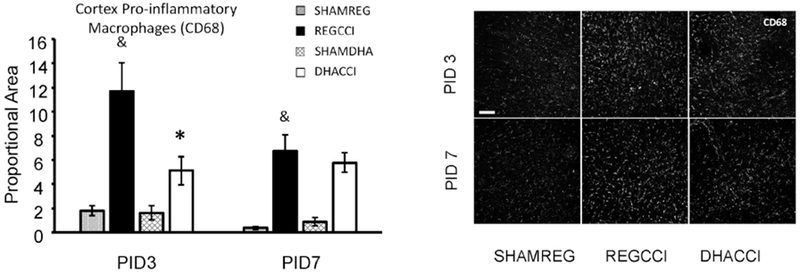
Results for cortical CD68 reactivity proportional area at PID 3 and PID 7 are shown graphically on the left. REGCCI and DHACCI are shown in solid black and white bars, respectively, while corresponding SHAM groups are shown as spotted gray and latticed white for SHAMREG and SHAMDHA rats. CCI increased CD68 immunoreactivity compared to SHAM controls (&p<0.0001, main effect of injury) with significant increases at both PID 3 (p=0.0001) and PID 7 (p=0.005). DHA significantly decreased CD68+ microglia/macrophage activation in the cortex (*p=0.03, main effect of treatment) with significant differences between REGCCI and DHACCI at PID3 (*p=0.02). In the hippocampus, CCI did not significantly increase CD68 (p=0.08), and there was no effect of DHA on CD68 expression after CCI (p=0.21, main effect of treatment). On the right, representative images of cortical CD68 reactivity are shown for SHAMREG, REGCCI and DHACCI. The scale bar is 100 microns.
