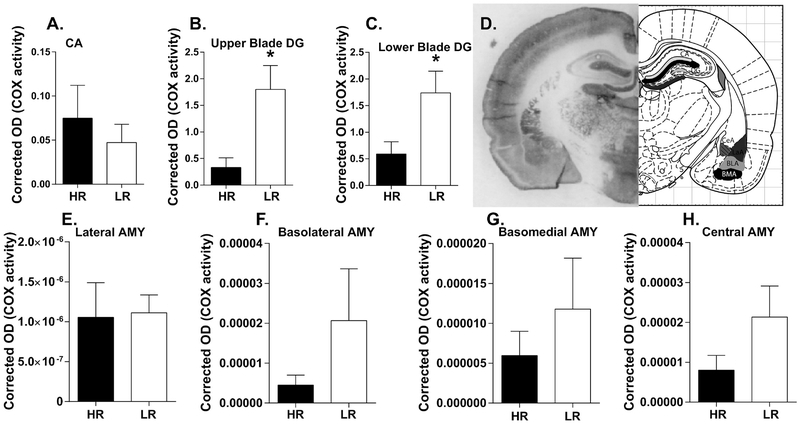
Figure 3. Cytochrome C oxidase (COX) activity in adult HR/LR hippocampus and amygdala.
(A-C) COX activity was assessed in the innermost molecular layer of the cornu ammonis (CA) region, where many hippocampal neurons form synapses (A), as well as in the upper blade (B) and lower blade (C) of dentate gyrus (DG). (D) Representative image of brain tissue processed for the in situ COX assay at the level of rostral hippocampus and amygdala (bregma −2.04 mm) Regions of interest are shown in black and grey on corresponding atlas images, which were adapted from “The Rat Brain” (6th Edition) by Paxinos & Watson). (E-H) COX activity was also measured in four nuclei of the amygdala: the lateral amygdala (LA; E); basolateral amygdala (BLA; F); basomedial amygdala (BMA; G); and Central amygdala (CeA; H). * indicates p-value < 0.05.