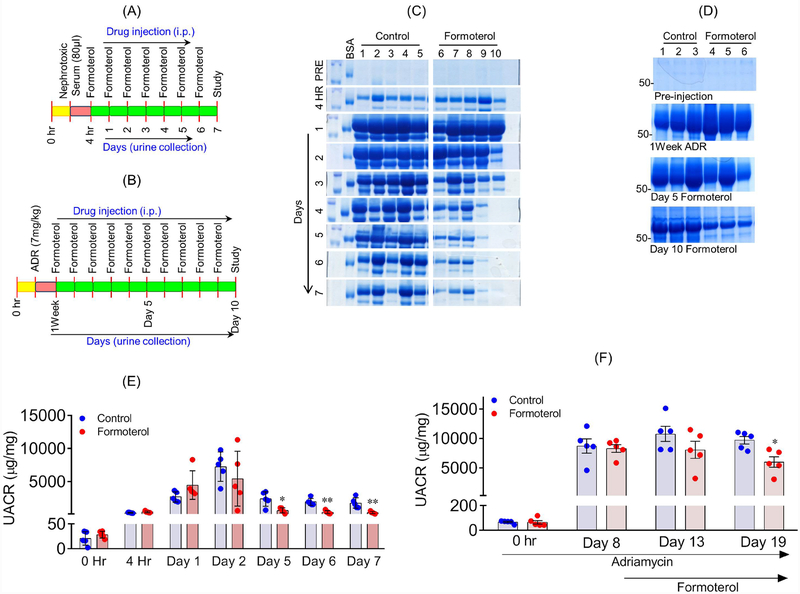
Figure 5: Formoterol accelerated glomerular recovery from acute and chronic models of glomerular injury:
The schematic of experimental plan to evaluate in-vivo significance of formoterol using NTS (A) and ADR (B) induced glomerular injury models. (C) Urine samples were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining and showed significant reduction in albuminuria starting at day3, which extended to day 7 in NTS+formoterol treated mice group, whereas minimal reduction was noted in the control NTS+vehicle treated mice group. (D) Similar urine analysis showed significant reduction in albuminuria at day 10 post formoterol treatment in ADR+formoterol treated mice, whereas minimal reduction was noted in the control ADR+vehicle mice. (E) Measurement of urine albumin/creatinine ratios by ELISA showed initiation of albuminuria at 4h post NTS injection, which further increased at days 1 and 2 in both groups. The ratios dropped to preinjection levels in NTS+formoterol treated mice group but remained significantly elevated in control mice group at days 5–7. 2-tailed t-test. n=5 mice per group. Data are presented in means±SEM. *P≤0.01, **P≤0.001 vs. control. (F) Measurements of urine albumin/creatinine ratios were made at 1 week post ADR-injection. The ratios remained significantly elevated in both the groups at day 5, but significant reduction was noted in ADR+formoterol mice at day 10 post formoterol treatment. 2-tailed t-test (*p<0.05, ADR+vehicle vs ADR+formoterol). n=5 mice per group. Data are presented as mean±SEM. In-vivo results were reproduced in three independent experiments with n=5, each group, each experiments.