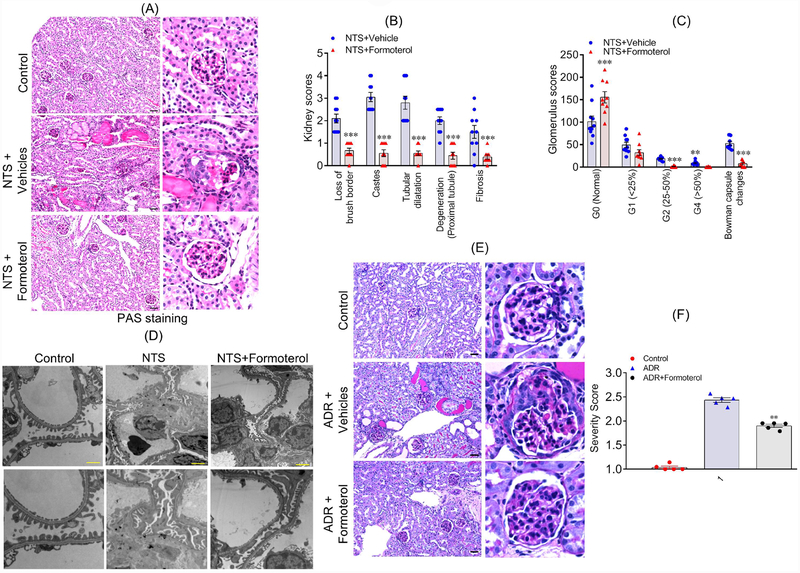
Figure 6: Formoterol restored injury-induced glomerular damage.
(A) Histological analysis of mice (sacrificed at day 7 post NTS injection) kidney sections shows that formoterol treatment (NTS+formoterol) reduced focal atrophy, proteinaceous tubular caste and tubular dilation as compared to control (vehicle) mice. Scale bar 50μm. (B) Major histological features were individually scored, and the comparative analysis showed reduction in loss of brush borders, degeneration of proximal tubules and reduced proteinaceous casts, tubular dilation and fibrosis in NTS+formoterol treated mice. 2-tailed t-test, ***P≤0.0001 NTS+vehicle vs. NTS+formoterol. (C) Glomerular scores demonstrating varying levels of glomerulosclerosis in control and NTS+formoterol treated mice are presented and show increased number of normal glomeruli in NTS+formoterol treated mice, along with reduction in sclerotic glomeruli. 2-tailed t-test, **P≤0.001, ***P≤0.0001 NTS+vehicle vs. NTS+formoterol. n=5 mice each group (both kidneys were scored) (D) Representative images from the TEM analysis show significant damage to podocyte foot processes in control NTS+vehicle treated mice, whereas, normal foot processes were present in the NTS+formoterol treated mice. Scale bar 2μm. (E) Histological analysis of mice (sacrificed at day 10 post formoterol injection) kidney sections showed that formoterol treatment (ADR+formoterol) reduced ADR-induced glomerular sclerosis, focal atrophy, proteinaceous tubular caste and tubular dilation. Scale bar 50μm. (F) Glomerulosclerosis severity score was calculated and was significantly reduced for ADR+formoterol mice. (**P≤0.001, NTS+vehicle vs. NTS+formoterol). n=5 mice each group.