Fig. 5.
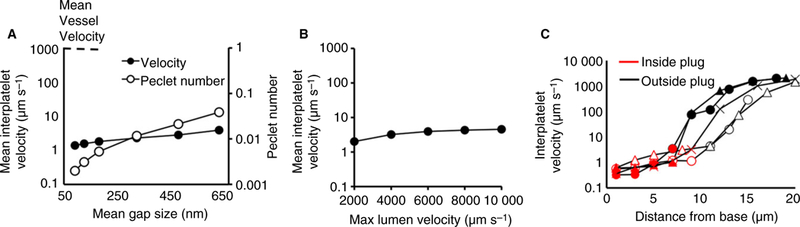
Determinants of interplatelet plasma velocity. (A) Over a biologically relevant range of gap sizes (60 to 600 nm), gap size has little effect on the interplatelet plasma velocity (filled circles, left vertical axis), and diffusion is the main driver of transport inside a hemostatic plug (empty circles, right vertical axis). (B) Increasing the maximum velocity in the vessel has little effect on the mean interplatelet velocity. (C) Interplatelet velocity measured at different points from the reconstruction of five actual hemostatic plug volumes. Each plug is indicated by a different symbol (empty triangles, empty circles, filled triangles, filled circles and crosses). On the outside of the plug (black points) plasma velocity is about 1 mm s−1, whereas in the inside of the plug (red points) the plasma velocity drops by three orders of magnitude.
