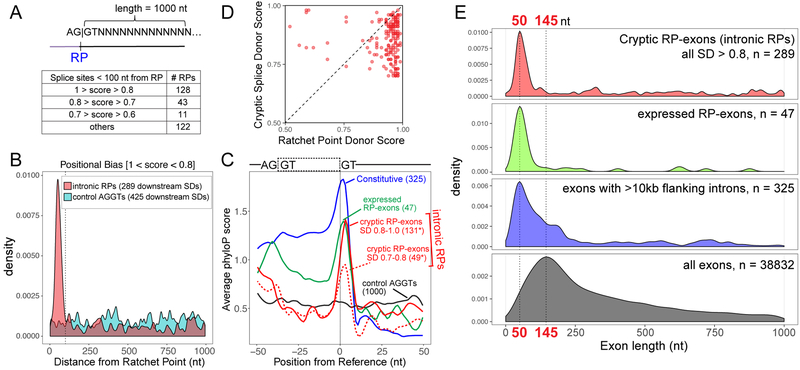
Figure 4. Genomewide identification of RP-associated cryptic exons.
(A) Schematic of strategy used to identify potential splice sites downstream of intronic RPs within a 1000nt window and a summary of non-overlapping RPs that were found to have high-scoring cryptic splice donors <100nt from the RPs. (B) Positional density of high-scoring splice donor sites downstream of intronic RPs (red) and control AGGT (cyan). A total of 289 SDs were found within a 1 kb region for all 304 RPs, whereas 485 SDs were found within a 1 kb region of 1000 control AGGT sites. Distance of splice site from RP is indicated on the x-axis and the dotted line marks 100nt from RPs. Similar positional bias was observed for lower-scoring bins of cryptic splice donors (Supplementary Figure 9). (C) Evolutionary conservation of splice donors from constitutive exons [with flanking intron length >10 kb] (blue), RP-exons (green) and potential cryptic exons [SDs <100nt from intronic RPs] (red line – high score splice sites, red dotted line – moderate score splice sites). *Note that some intronic RPs had >1 high scoring SD within 100nt. (D) Cryptic splice donors are generally weaker than their paired RP donors. Each dot represents the NNSPLICE scores predicted at a given intronic recursive site; only the highest-scoring (>0.7) cryptic splice donors <100 nt from RPs were considered in this analysis. (E) Preferred length of exon definition for cryptic RP-exons, RP-exon and constitutive exons within long intronic contexts. Plotted are exon lengths inferred from intronic RPs + cryptic donor (red), RP-exons (green), constitutive exons with flanking intron length >10 kb (blue) and all Drosophila exons with flanking introns (black). In the case of intronic RPs, all SDs (>0.8 score) found within 1 kb of RPs were used to generate positional density plots (B, E); however, only proximal SDs are predominantly likely to contribute to cryptic exon processing.