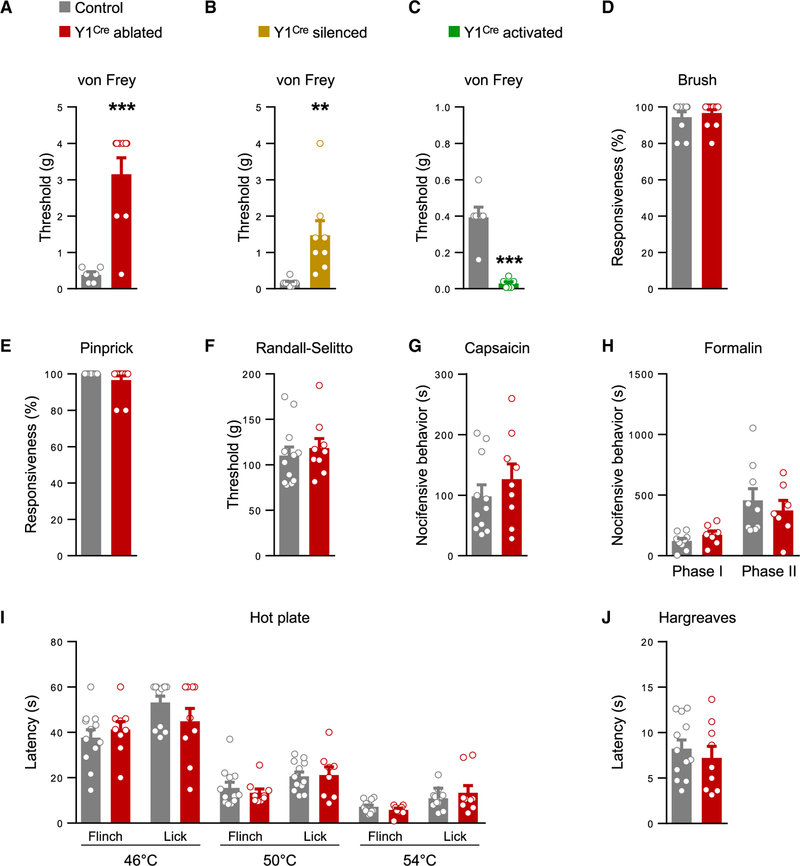
Figure 4. Y1Cre Neurons Selectively Transmit Light Touch Information.
(A and B) Sensitivity to von Frey hair stimulation of the hindpaw glabrous skin is reduced following Y1Cre neuron ablation (A; control, n = 6; ablated, n = 9) or silencing (B; control, n = 8; silenced, n = 8).
(C) Glabrous skin sensitivity to von Frey hair stimulation is elevated following Y1Cre neuron activation (control, n = 6; activated, n = 6).
(D–F) Responses to dynamic touch (D; control, n = 11; ablated, n = 13), pinprick (E; control, n = 11; ablated, n = 13), and Randall-Selitto (F; control, n = 12; ablated, n = 9) are unchanged after Y1Cre neuron ablation.
(G and H) Chemical pain responses following hindpaw injection of capsaicin (G; control, n = 11; ablated, n = 9) or formalin (H; control, n = 9; ablated, n = 7) are not altered following Y1Cre neuron ablation.
(I and J) Y1Cre neuron-ablated mice show normal heat responses as assessed by the hot plate (I; control, n = 12; ablated, n = 9) and Hargreaves (J; control, n = 12; ablated, n = 9) assays.
**p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Data: mean ± SEM.