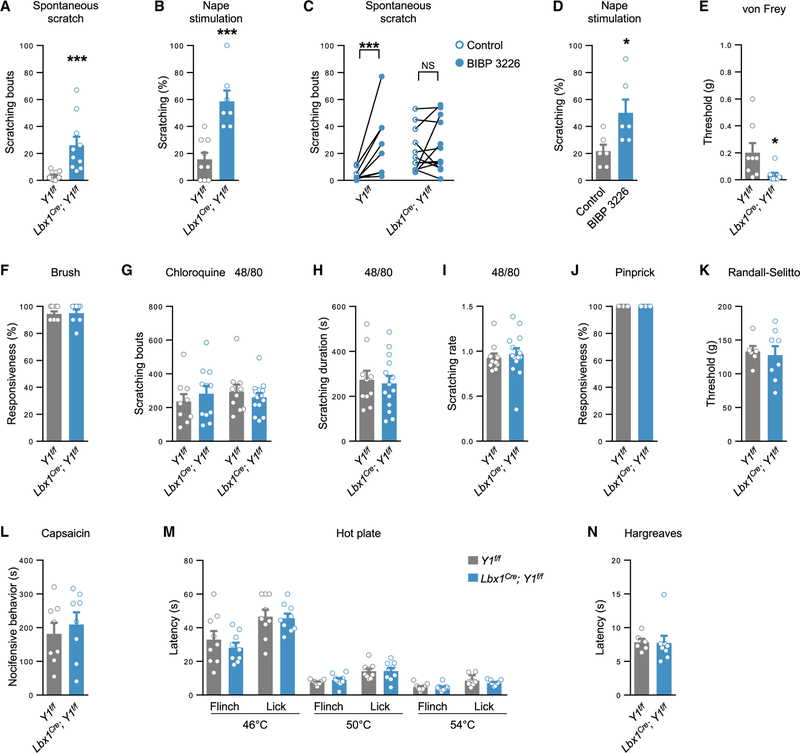
Figure 6. NPY-Y1 Receptor Signaling within the Dorsal Horn Gates Mechanical Itch and Light Punctate Touch.
(A and B) Mice lacking the Y1 receptor in dorsal horn neurons exhibit pronounced spontaneous scratching (A; Lbx1Cre; Y1f/f, n = 10; Y1f/f control, n = 12) and hypersensitivity to light punctate mechanical stimulation of the nape (B; Lbx1Cre; Y1f/f,n = 7; Y1f/f control, n = 9).
(C) The Y1 antagonist BIBP 3226 (1 mg kg−1, intraperitoneally [i.p.]) increases spontaneous scratching in control (n = 8) but not conditional knockout mice (n = 12). Two-tailed, paired t tests were used to assess statistical differences.
(D) BIBP 3226 causes hypersensitivity to nape stimulation (n = 12; vehicle, n = 12).
(E and F) Lbx1Cre; Y1f/f mice have reduced hindpaw von Frey thresholds (E; Lbx1Cre; Y1f/f,n= 8; Y1f/f control, n = 8) but responses to dynamic touch are unaltered (F; Lbx1Cre; Y1f/f,n= 8; Y1f/f control, n = 9).
(G–I) Deletion of Y1 from dorsal horn neurons does not alter scratching frequency in response to chloroquine (Lbx1Cre; Y1f/f, n = 11; Y1f/f control, n = 9) or scratching frequency (G), duration (H), or rate (duration/frequency; I) in response to compound 48/80 (Lbx1Cre; Y1f/f, n = 14; Y1f/f control, n = 10).
(J–N) Deletion of Y1 from dorsal horn neurons does not affect sensitivity to acute mechanical pain as assessed by pinprick (J; Lbx1Cre; Y1f/f,n = 9; Y1f/f control, n = 9) or the Randall-Selitto test (K; Lbx1Cre; Y1f/f,n= 8; Y1f/f control, n = 6), chemical nociception (L; Lbx1Cre; Y1f/f,n= 8; Y1f/f control, n = 8), or thermal pain as assessed by the hot plate (M; Lbx1Cre; Y1f/f,n = 9; Y1f/f control, n = 9) or Hargreaves tests (N; Lbx1Cre; Y1f/f,n = 8; Y1f/f control, n = 6).
*p < 0.05 and ***p < 0.001. NS, not significant. Data: mean ± SEM.