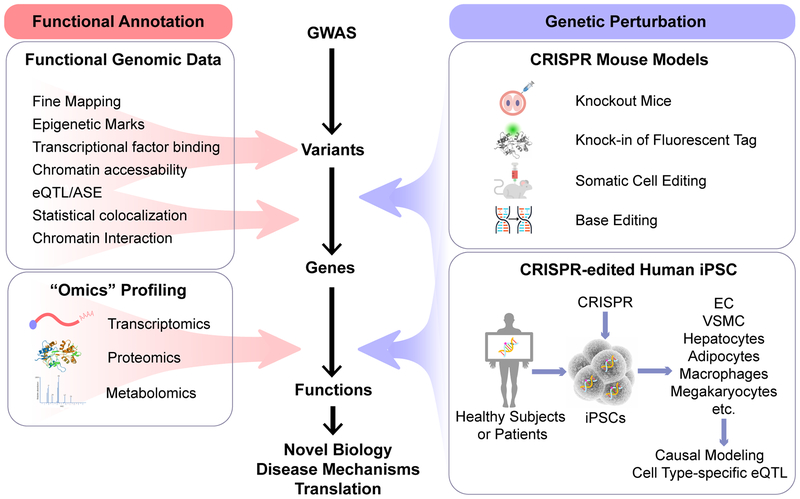
Figure 1. Interpreting GWAS findings with functional genomic tools for novel biology and translation.
Functional genomic data are essential for the functional annotation and prioritization of potential causal variants and genes. Perturbation of the candidate variants and genes in relevant tissues and cell types or model organisms establishes the causality and biological mechanisms of the variant-disease association. Integrating “omics” profiling facilitates hypothesis generation and mechanistic studies. ASE, allele-specific expression; CRISPR, clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats; eQTL, expression quantitative trait loci; GWAS, genome-wide association studies; iPSC, induced pluripotent stem cells.