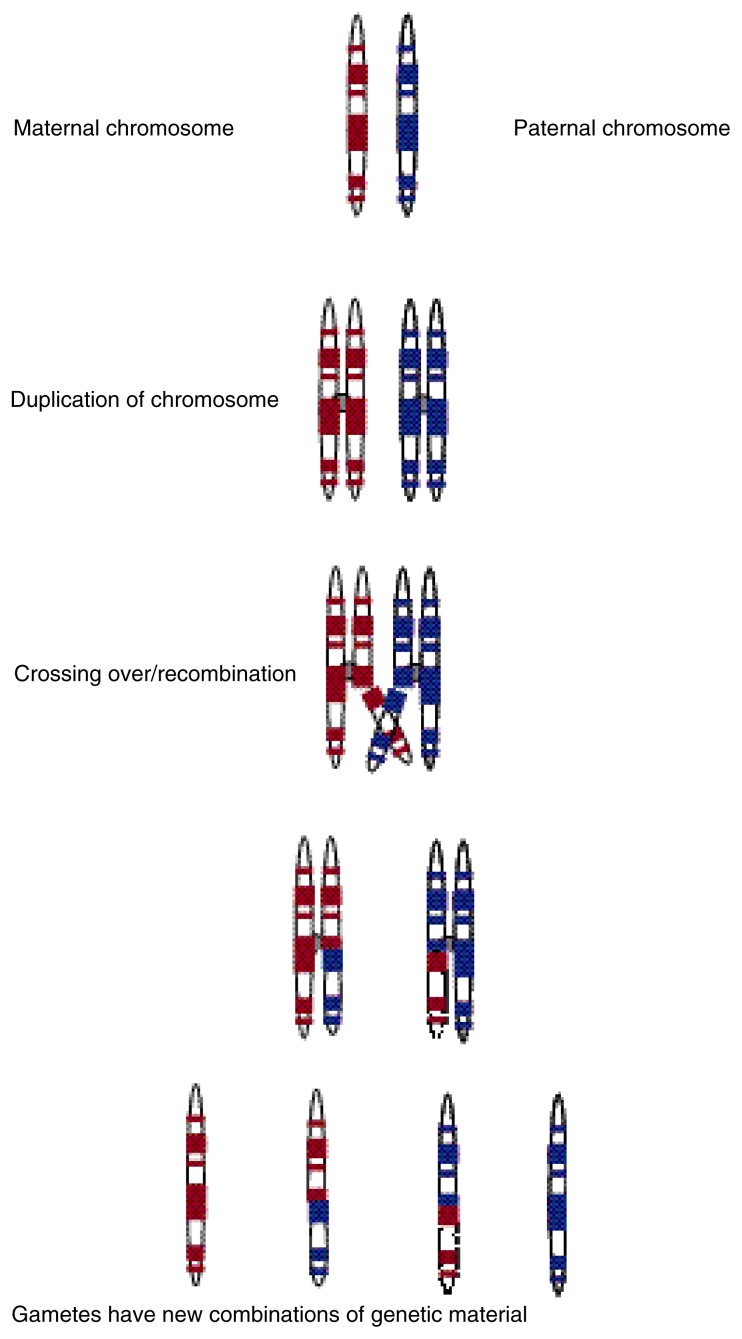
Figure 2.
Crossing over and genetic recombination during the specialized cell division (i.e., meiosis) that results in the production of sperm or egg cells (i.e., the gametes). Each member of each chromosome pair (i.e., the one inherited from the mother and the one inherited from the father) duplicates itself, and genetic material may cross over. In inbred strains, in which each chromosome pair is identical, crossing over has no observable effect. In animals in which the maternal and paternal chromosomes are not identical (e.g., F1 animals), however, crossing over will result in the recombination of parental genes. Because of this recombination, all the genes on a chromosomes are not always inherited together.