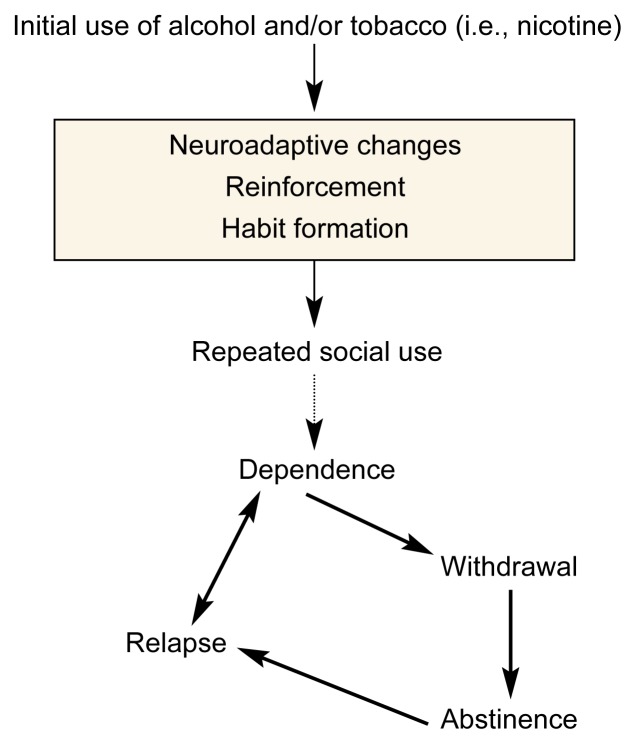
Figure 2.
Consequences of continued alcohol and tobacco (i.e., nicotine) use.
During the initial use of alcohol and tobacco, changes in the activity of nerve cells (i.e., neuroadaptive changes) occur, resulting in reinforcement and habit formation. These changes lead to repeated social use, which may result in dependence in some people. In those people, sudden abstinence from alcohol or nicotine leads to withdrawal symptoms, which cease during prolonged abstinence. However, even after prolonged abstinence, relapse may occur.