Fig. 6.
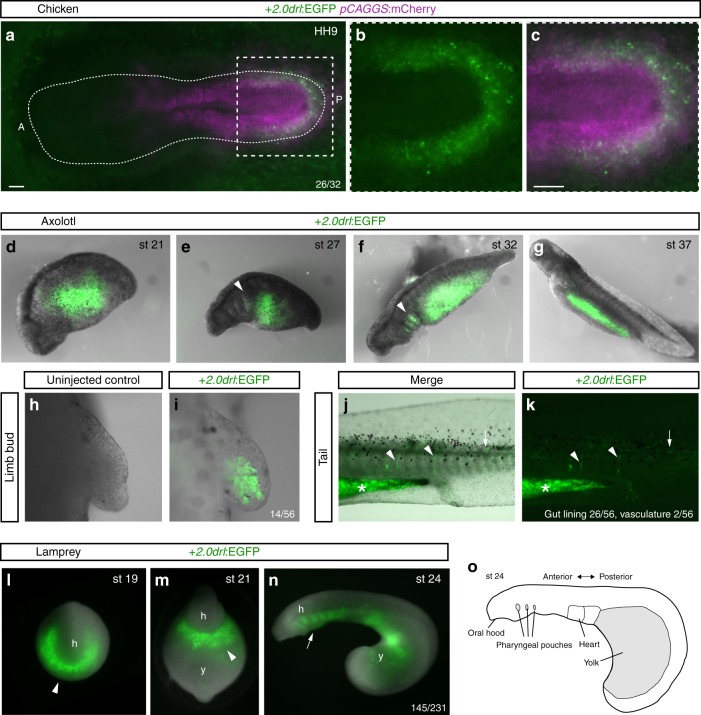
The zebrafish +2.0 drl enhancer reads out a LPM program across vertebrates. a–c Representative HH9 ex-ovo-cultured chicken embryo electroporated at HH3+/4 with +2.0drl:EGFP (green, a–c) and ubiquitous pCAGGS:mCherry control (magenta, a, c), showing specific +2.0drl reporter expression in the electroporated LPM (n = 26/32). The dashed line depicts the outline of the chicken embryo, anterior (A) to the left, posterior (P) to the right; boxed region (a) depicts magnified area shown for single and merged channels (b, c). d–k Expression of +2.0drl:EGFP upon transient injections in axolotl at the indicated embryonic stages. Note EGFP expression in the lateral portion of the embryo, future gut region, and pharyngeal arches (arrowheads in e, f). h, i EGFP expression in mesenchymal cells of the developing axolotl limb bud, indicative of LPM origin (n = 14/56). j, k EGFP fluorescence in axolotl st 43 larvae in the gut lining (asterisk, n = 26/56) and blood vessels (arrowheads, n = 2/56). Expression is also found occasionally in a small fraction of muscle fibers (arrows). l–o Transient transgenic lamprey embryos (Petromyzon marinus) with +2.0drl:EGFP expression in the anterior mesendoderm (arrowheads) and overlying the yolk at neurula stages (st 19–21) (l, m), and in the developing pharynx (arrow) during head protrusion (st 23–24) (n); views anterior (l), ventral (m), lateral (n), head (h) and yolk (y) (n = 145/231). o Schematic depiction of st 23 lamprey embryo to outline key features. Scale bar (a, c) 250 μm