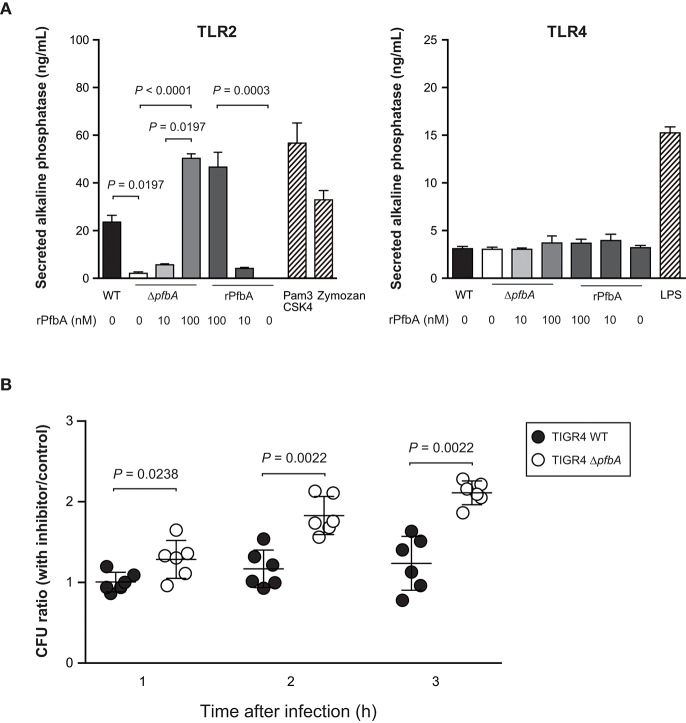
Figure 4.
PfbA activates NF-κB via TLR2 and TLR2/4 inhibitor enhances ΔpfbA strain survival. (A) Secreted alkaline phosphatase (SEAP) porter assay using TLR2/NF-κB/SEAPorter or TLR4/MD-2/CD14/NF-κB SEAPorter HEK293 cell lines. The cells were plated in 24-well plates at 5 × 105 cells/well. After 24 h, cells were stimulated with various amount of rPfbA, pasteurized S. pneumoniae (~5 × 106 CFU), 1 μg/mL Pam3CSK4, 10 μg/mL Zymozan, or 25 ng/mL LPS for 24 h. SEAP was analyzed using the SEAPorter Assay Kit. Data are presented as the mean of six wells. SE values are represented by vertical lines. Differences in pneumococcal infection group and rPfbA addition group were analyzed using a Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn's multiple comparisons test, respectively. (B) TLR2/4 inhibitor peptide enhances survival of the TIGR4 ΔpfbA strain incubated with human neutrophils. S. pneumoniae TIGR4 wild type strain or ΔpfbA strain bacteria were incubated with human neutrophils in the presence of TLR2/4 inhibitor peptide or control peptide. After 1, 2, and 3 h, the mixture was serially diluted and plated on TS blood agar. Following incubation, the number of CFUs was determined. The CFU ratio was calculated by dividing CFUs in the presence of inhibitor peptide by CFUs in the presence of control peptide. Data are presented as the mean of six wells. S.E. values are represented by vertical lines. Differences between groups were analyzed using Mann-Whitney's U-test.