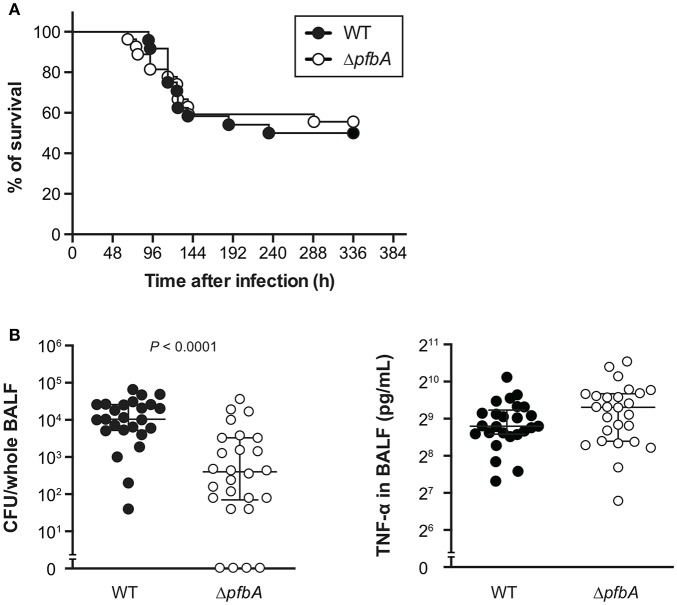
Figure 5.
In a mouse pneumonia model, deficiency of pfbA decreases pneumococcal burden in the lung but does not affect host mortality. (A) CD-1 mice were infected intratracheally with the S. pneumoniae TIGR4 wild-type or ΔpfbA strain (3–18 × 106 CFUs). Mice survival was recorded for 14 days. The differences between groups were analyzed using a log-rank test. (B) Bacterial CFUs and TNF-α in BALF collected from CD-1 mice after intratracheal infection with S. pneumoniae. CD-1 mice were infected intratracheally with the S. pneumoniae TIGR4 wild type or ΔpfbA strain (4–7 × 106 CFUs). BALF was collected at 24 h after pneumococcal infection, and bacterial CFUs and TNF-α levels in the BALF were determined. The median and interquartile range (IQR) values are represented by vertical lines. Statistical differences between groups were analyzed using Mann-Whitney's U-test. The data obtained from three independent experiments were pooled.